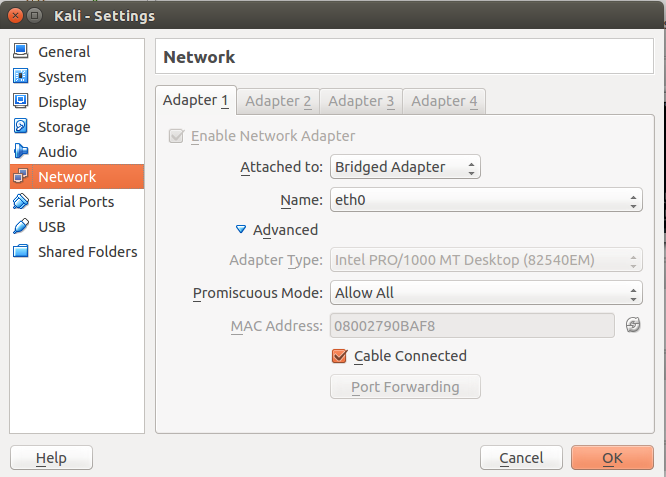
0.Configure Guest OS via Virtualbox as follows.
VirtualBox Manager > Settings > Network
Attached to: Bridged Adapter
Name : eth0
Advanced:
Promiscuous Mode: Allow All
1.Install telnet use this command in main OS terminal:
sudo apt-get install xinetd telnetd
2.Edit /etc/inetd.conf in main OS using your favourite file editor with root permission,add this line:
telnet stream tcp nowait telnetd /usr/sbin/tcpd /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
3.Edit /etc/xinetd.conf in main OS,make its content look like following:
Simple configuration file for xinetd
#
# Some defaults, and include /etc/xinetd.d/
defaults
{
# Please note that you need a log_type line to be able to use log_on_success
# and log_on_failure. The default is the following :
# log_type = SYSLOG daemon info
instances = 60
log_type = SYSLOG authpriv
log_on_success = HOST PID
log_on_failure = HOST
cps = 25 30
}
4.Use this command to start telnet server in main OS:
sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd restart
That was all. By the way, this configuration will affect just main OS which you use instead of Guest OS. That is, you can create a telnet connection just from Guest OS's terminal to main OS, not from main OS to Guest OS. Because, telnet server is in main OS. To be able to do two way telnet communication, you should repeat the steps above in Guest OS's terminal.
Resource : http://ubuntuguide.net/install-and-enable-telnet-server-in-ubuntu-linux

sshhas been long preferred over the deprecated telnet. – Rodeo