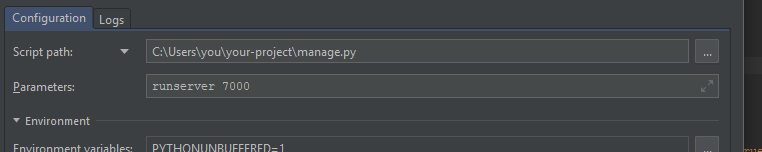
I would like to make the default port that manage.py runserver listens on specifiable in an extraneous config.ini. Is there an easier fix than parsing sys.argv inside manage.py and inserting the configured port?
The goal is to run ./manage.py runserver without having to specify address and port every time but having it take the arguments from the config.ini.