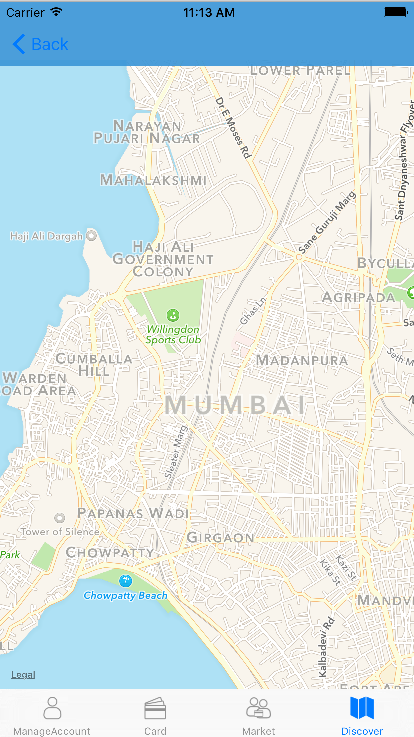
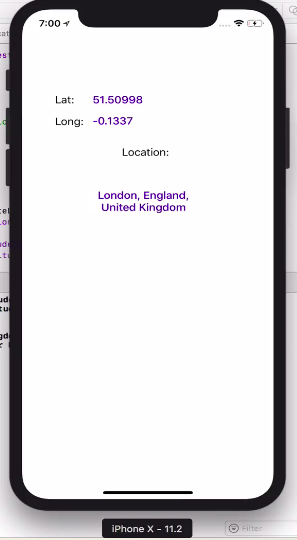
First import Corelocation and MapKit library:
import MapKit
import CoreLocation
inherit from CLLocationManagerDelegate to our class
class ViewController: UIViewController, CLLocationManagerDelegate
create a locationManager variable, this will be your location data
var locationManager = CLLocationManager()
create a function to get the location info, be specific this exact syntax works:
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
in your function create a constant for users current location
let userLocation:CLLocation = locations[0] as CLLocation // note that locations is same as the one in the function declaration
stop updating location, this prevents your device from constantly changing the Window to center your location while moving (you can omit this if you want it to function otherwise)
manager.stopUpdatingLocation()
get users coordinate from userLocatin you just defined:
let coordinations = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: userLocation.coordinate.latitude,longitude: userLocation.coordinate.longitude)
define how zoomed you want your map be:
let span = MKCoordinateSpanMake(0.2,0.2)
combine these two to get region:
let region = MKCoordinateRegion(center: coordinations, span: span)//this basically tells your map where to look and where from what distance
now set the region and choose if you want it to go there with animation or not
mapView.setRegion(region, animated: true)
close your function
}
from your button or another way you want to set the locationManagerDeleget to self
now allow the location to be shown
designate accuracy
locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest
authorize:
locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
to be able to authorize location service you need to add these two lines to your plist
![enter image description here]()
get location:
locationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
show it to the user:
mapView.showsUserLocation = true
This is my complete code:
import UIKit
import MapKit
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController, CLLocationManagerDelegate {
@IBOutlet weak var mapView: MKMapView!
var locationManager = CLLocationManager()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() {
super.didReceiveMemoryWarning()
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@IBAction func locateMe(sender: UIBarButtonItem) {
locationManager.delegate = self
locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest
locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
locationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
mapView.showsUserLocation = true
}
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
let userLocation:CLLocation = locations[0] as CLLocation
manager.stopUpdatingLocation()
let coordinations = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: userLocation.coordinate.latitude,longitude: userLocation.coordinate.longitude)
let span = MKCoordinateSpanMake(0.2,0.2)
let region = MKCoordinateRegion(center: coordinations, span: span)
mapView.setRegion(region, animated: true)
}
}