Your solution would work at orthographic projection, but it fails at perspective projection. Note, at Perspective Projection the projection matrix describes the mapping from 3D points in the world as they are seen from of a pinhole camera, to 2D points of the viewport.
The amount of displacement for the eye and target position depends on the depth of the object which is dragged on the viewport.
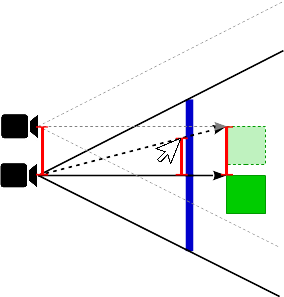
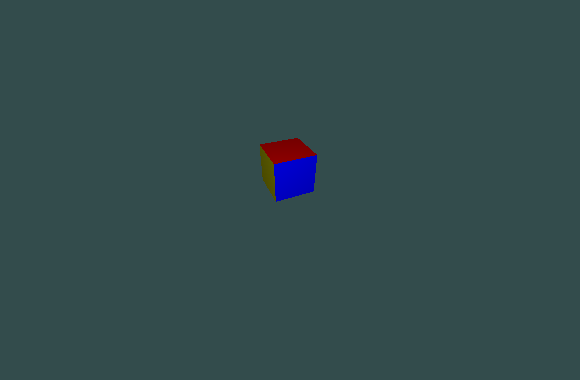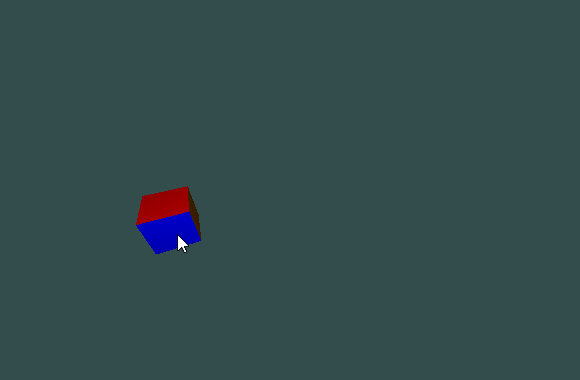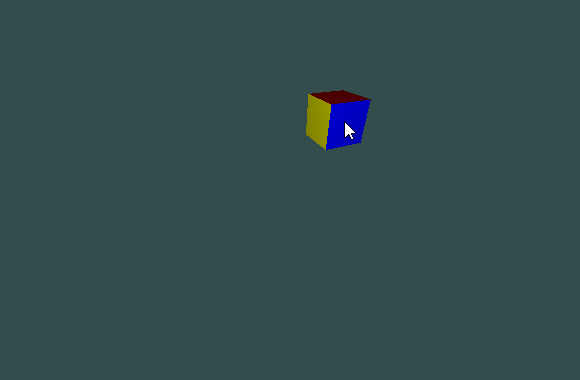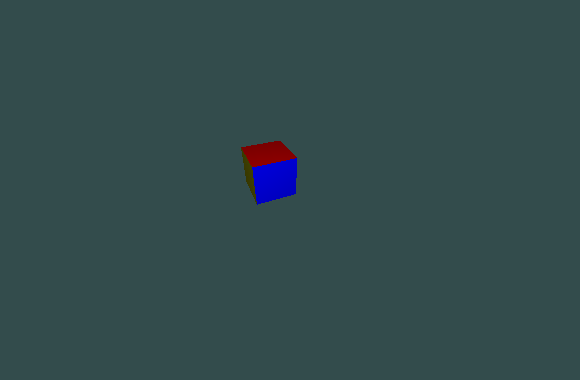
If the object is close to the eye position, then a translation on the viewport leads to a small displacement of the eye and target positions:
![]()
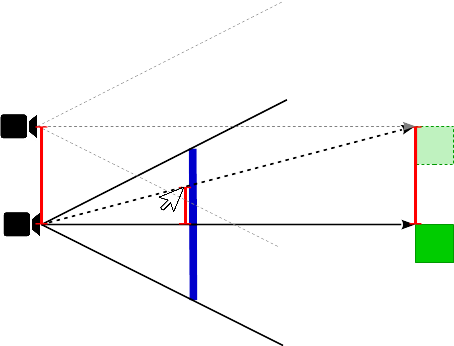
If the distance from the object to the eye is far, then a translation on the viewport leads to a large displacement of the eye and target positions:
![]()
To do what you want you have to know the size of the viewport, the view matrix and the projection matrix:
self.width # width of the viewport
self.height # height of the viewport
self.view # view matrix
self.proj # prjection matrix
Change the pane method, so that it receives the new and old mouse position. Note y axis has to be flipped (self.height-y). Get the depth of the hit point (object) by glReadPixels using the format type GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT:
def glut_mouse(self, button, state, x, y):
self.drag = state == GLUT_DOWN
self.last_mouse_pos = glm.vec2(x, self.height-y)
self.mouse_down_pos = glm.vec2(x, self.height-y)
if self.drag:
depth_buffer = glReadPixels(x, self.height-y, 1, 1, GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT, GL_FLOAT)
self.last_depth = depth_buffer[0][0]
print(self.last_depth)
def glut_motion(self, x, y):
if not self.drag:
return
old_pos = self.last_mouse_pos
new_pos = glm.vec2(x, self.__vp_size[1]-y)
self.last_mouse_pos = new_pos
self.pan(self.last_depth, old_pos, new_pos)
def pan(self, depth, old_pos, new_pos):
# .....
The mouse position gives a position in window space, where the z coordinate is the depth of the hit point respectively object:
wnd_from = glm.vec3(old_pos[0], old_pos[1], float(depth))
wnd_to = glm.vec3(new_pos[0], new_pos[1], float(depth))
This positions can be transformed to world space by glm.unProject:
vp_rect = glm.vec4(0, 0, self.width, self.height)
world_from = glm.unProject(wnd_from, self.view, self.proj, vp_rect)
world_to = glm.unProject(wnd_to, self.view, self.proj, vp_rect)
The world space displacement of the eye and target position is the distance from the old to the new world position:
world_vec = world_to - world_from
Finally calculate the new eye and target position and update the view matrix:
self.eye = self.eye - world_vec
self.target = self.target - world_vec
self.view = glm.lookAt(self.eye, self.target, self.up)
See also Python OpenGL 4.6, GLM navigation
I tested the code with the following example:
Preview:
![]()
Full python code:
import os
import math
import numpy as np
import glm
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GL.shaders import *
from OpenGL.arrays import *
from ctypes import c_void_p
class MyWindow:
__caption = 'OpenGL Window'
__vp_size = [800, 600]
__vp_valid = False
__glut_wnd = None
__glsl_vert = """
#version 450 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 a_pos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 a_nv;
layout (location = 2) in vec4 a_col;
out vec3 v_pos;
out vec3 v_nv;
out vec4 v_color;
uniform mat4 u_proj;
uniform mat4 u_view;
uniform mat4 u_model;
void main()
{
mat4 model_view = u_view * u_model;
mat3 normal = transpose(inverse(mat3(model_view)));
vec4 view_pos = model_view * vec4(a_pos.xyz, 1.0);
v_pos = view_pos.xyz;
v_nv = normal * a_nv;
v_color = a_col;
gl_Position = u_proj * view_pos;
}
"""
__glsl_frag = """
#version 450 core
out vec4 frag_color;
in vec3 v_pos;
in vec3 v_nv;
in vec4 v_color;
void main()
{
vec3 N = normalize(v_nv);
vec3 V = -normalize(v_pos);
float ka = 0.1;
float kd = max(0.0, dot(N, V)) * 0.9;
frag_color = vec4(v_color.rgb * (ka + kd), v_color.a);
}
"""
__program = None
__vao = None
__vbo = None
__no_vert = 0
def __init__(self, w, h):
self.__vp_size = [w, h]
glutInit()
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH)
glutInitWindowSize(self.__vp_size[0], self.__vp_size[1])
__glut_wnd = glutCreateWindow(self.__caption)
self.__program = compileProgram(
compileShader( self.__glsl_vert, GL_VERTEX_SHADER ),
compileShader( self.__glsl_frag, GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER ),
)
self.___attrib = { a : glGetAttribLocation (self.__program, a) for a in ['a_pos', 'a_nv', 'a_col'] }
print(self.___attrib)
self.___uniform = { u : glGetUniformLocation (self.__program, u) for u in ['u_model', 'u_view', 'u_proj'] }
print(self.___uniform)
v = [ -1,-1,1, 1,-1,1, 1,1,1, -1,1,1, -1,-1,-1, 1,-1,-1, 1,1,-1, -1,1,-1 ]
c = [ 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 ]
n = [ 0,0,1, 1,0,0, 0,0,-1, -1,0,0, 0,1,0, 0,-1,0 ]
e = [ 0,1,2,3, 1,5,6,2, 5,4,7,6, 4,0,3,7, 3,2,6,7, 1,0,4,5 ]
attr_array = []
for si in range(6):
for vi in range(6):
ci = [0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3][vi]
i = si*4+ci
attr_array.extend( [ v[e[i]*3], v[e[i]*3+1], v[e[i]*3+2] ] )
attr_array.extend( [ n[si*3], n[si*3+1], n[si*3+2] ] )
attr_array.extend( [ c[si*3], c[si*3+1], c[si*3+2], 1 ] );
self.__no_vert = len(attr_array) // 10
vertex_attributes = np.array(attr_array, dtype=np.float32)
self.__vbo = glGenBuffers(1)
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, self.__vbo)
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertex_attributes, GL_STATIC_DRAW)
self.__vao = glGenVertexArrays(1)
glBindVertexArray(self.__vao)
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, False, 10*vertex_attributes.itemsize, None)
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0)
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, False, 10*vertex_attributes.itemsize, c_void_p(3*vertex_attributes.itemsize))
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1)
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 4, GL_FLOAT, False, 10*vertex_attributes.itemsize, c_void_p(6*vertex_attributes.itemsize))
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2)
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST)
glUseProgram(self.__program)
glutReshapeFunc(self.__reshape)
glutDisplayFunc(self.__mainloop)
glutMouseFunc(self.glut_mouse)
glutMotionFunc(self.glut_motion)
self.drag = False
self.eye = glm.vec3(-3, -7, 6)
self.target = glm.vec3(0, 0, 0)
self.up = glm.vec3(0, 0, 1)
self.near = 0.1
self.far = 100.0
aspect = self.__vp_size[0]/self.__vp_size[1]
self.proj = glm.perspective(glm.radians(90.0), aspect, self.near, self.far)
self.view = glm.lookAt(self.eye, self.target, self.up)
self.model = glm.mat4(1)
def run(self):
self.__starttime = 0
self.__starttime = self.elapsed_ms()
glutMainLoop()
def elapsed_ms(self):
return glutGet(GLUT_ELAPSED_TIME) - self.__starttime
def __reshape(self, w, h):
self.__vp_valid = False
def __mainloop(self):
if not self.__vp_valid:
self.width = glutGet(GLUT_WINDOW_WIDTH)
self.height = glutGet(GLUT_WINDOW_HEIGHT)
self.__vp_size = [self.width, self.height]
self.__vp_valid = True
aspect = self.width / self.height
self.proj = glm.perspective(glm.radians(90.0), aspect, self.near, self.far)
glUniformMatrix4fv(self.___uniform['u_proj'], 1, GL_FALSE, glm.value_ptr(self.proj) )
glUniformMatrix4fv(self.___uniform['u_view'], 1, GL_FALSE, glm.value_ptr(self.view) )
glUniformMatrix4fv(self.___uniform['u_model'], 1, GL_FALSE, glm.value_ptr(self.model) )
glClearColor(0.2, 0.3, 0.3, 1.0)
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, self.__no_vert)
glutSwapBuffers()
glutPostRedisplay()
def glut_mouse(self, button, state, x, y):
self.drag = state == GLUT_DOWN
self.last_mouse_pos = glm.vec2(x, self.height-y)
self.mouse_down_pos = glm.vec2(x, self.height-y)
if self.drag:
depth_buffer = glReadPixels(x, self.height-y, 1, 1, GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT, GL_FLOAT)
self.last_depth = depth_buffer[0][0]
print(self.last_depth)
def glut_motion(self, x, y):
if not self.drag:
return
old_pos = self.last_mouse_pos
new_pos = glm.vec2(x, self.__vp_size[1]-y)
self.last_mouse_pos = new_pos
self.pan(self.last_depth, old_pos, new_pos)
def pan(self, depth, old_pos, new_pos):
wnd_from = glm.vec3(old_pos[0], old_pos[1], float(depth))
wnd_to = glm.vec3(new_pos[0], new_pos[1], float(depth))
vp_rect = glm.vec4(0, 0, self.width, self.height)
world_from = glm.unProject(wnd_from, self.view, self.proj, vp_rect)
world_to = glm.unProject(wnd_to, self.view, self.proj, vp_rect)
world_vec = world_to - world_from
self.eye = self.eye - world_vec
self.target = self.target - world_vec
self.view = glm.lookAt(self.eye, self.target, self.up)
window = MyWindow(800, 600)
window.run()

selfand its fields + behaviours e.g. how theeyeandtargetfields are used to calculate the camera matrix. – Pennoncel