I am new to hybris, What is diff b/w relations and collections, why we go for relations instead of collections.
Basically, there are two technically different ways of modeling collections in hybris:
CollectionTypes
- Think of CollectionTypes in hybris as a backpack mounted onto a type
- By runtime, CollectionTypes are resolved into a Collection of a kind of item, such as a List of MediaModels
- Can cause overflow, resulting in truncation and therefore loss of data
- More difficult to search and lower performance
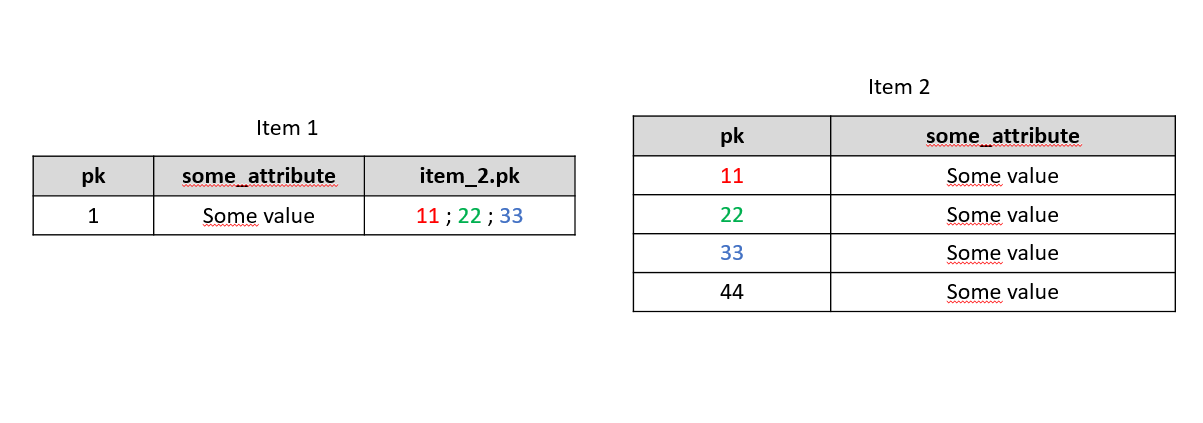
- On the database level, CollectionTypes are a comma-separated list of PKs, so there is a maximum
RelationTypes
- Create links between all kinds of types Create type-safe n-to-m relations: Only link such elements of the source / target type declared at the relation
- Values for relations are stored in a separate database table +Each value is stored in a separate table row
As Sumit says above,
CollectionType is discouraged and RelationType should be used whenever possible. This is because, the maximum length of the database field of a CollectionType is limited and a CollectionType with many values may end up getting its values truncated. In addition, the values of CollectionTypes are written in a CSV format and not in a normalized way. By consequence, hybris recommends using RelationTypes whenever possible.
- CollectionType: CollectionTypes are based on the Java Collection class i.e. a Collection is a list of elements.
1:n - Keep links to the respective values via an attribute on the source item, for example, a list of Primary Keys.
n:1 - Store the attribute values at the respective target items and have a getter method at the source type to retrieve the values. - RelationType:
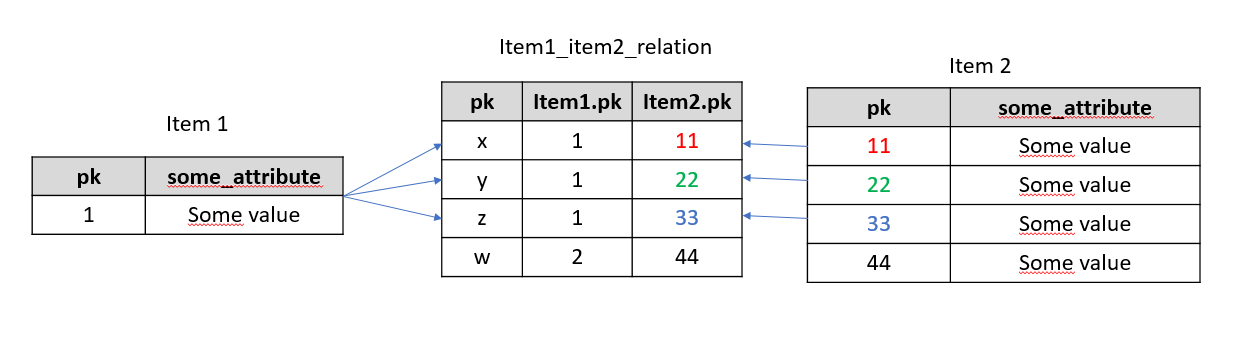
n:m - Internally, the elements on both sides of the relation are linked together via instances of a helper type called LinkItem. LinkItems hold two attributes, SourceItem and TargetItem, that hold references to the respective item.
For each entry within a relation (in other words, for each link from one item to another), there is a LinkItem instance that stores the PKs of the related items. LinkItem instances are handled transparently and automatically by the platform: On the API level, you only need to use the respective getter and setter methods.
Its important to understand hybris strongly discourages using collections, use relations instead.
As stated above collections are maintained as comma separated from a data structure prospective and thats why you might see problem of data truncate, where as relations have rational data structure of creating a new table and map table to join the two table.
Collection because of there storage structure - can't be searched.
I would say for a very simple (1:n) relationship with limited data - you can still use collections. While for any complex (m:n /1:n) relationship always use relations
In collections we have limited size, If we are trying to insert more data it will be truncated. Relations we can use n no. of data.
Collections is faster than relations, but in collections we can use only one to many relationship only, for many to many we should use relations only....
Adding to what Raghav has added, a collection internally is stored as a csv of the PKs in a single column. Hence the size limit due to field length restriction in any database.
A relation however can be stored in a separate table and hence unlimited mappings can be done.
Collection The Root Interface in the Collection Hierarchy.
Collection represents a group of objects, known as its elements.
Some collections allow Duplicate elements and others do Not.
Some are Ordered and others Un-Ordered
To get a really good idea of what each collection is good for and their performance characteristics I would recommend getting a good idea about Data Structures like Arrays, Linked Lists, Binary Search Trees, Hashtables, as well as Stacks and Queues. There is really no substitute to learning this if you want to be an Effective Programmer in any Language.
HashMap is only really used for cases when there is some logical reason to have special keys corresponding to values
Collections are persisted as a serialized object in a single column in the DB.
Relations are persisted in the usual relational database way - using a foreign key on another table or a link table (depending on the cardinality of the relation)
Collection types are discouraged as they cannot be searched using flexiblesearch and have significant performance limitations when dealing with collections of more than a handful of objects.
The exact difference between Collection and Relations in hybris is:
"How the data is stored in both of them"
In collections, a new column is created in table(item), containing comma separated primary keys of the list elements. The actual list elements are stored in another table.
In relations, a new table is created as a link table between two item types.
You can read the complete difference here.
One to many relationship can be achieved by Collection and relation and
Why collection is preferred in some cases over relation in Hybris
Collection - an alternative to one to many relation
Example: User and Address
Here Address is of type Collection and mapped to User as AddressCollection. User must need an address object but for address it is not neccessary to have UserModel reference (an user can have many addresses). Here is why collection preferred than relation.
<collectiontype code="AddressCollection" elementtype="Address" autocreate="true" generate="false"/>
<itemtype code="User"
extends="Principal"
jaloclass="de.hybris.platform.jalo.user.User"
autocreate="true"
generate="true">
<deployment table="Users" typecode="4" propertytable="UserProps"/>
<attributes>
<attribute autocreate="true" qualifier="addresses" type="AddressCollection">
<modifiers read="true" write="true" search="false" optional="true" partof="true"/>
<persistence type="jalo"/>
</attribute>
</attributes>
</itemtype>
Relation - One to many
Example: User and Order
Here one User can place as many as orders he want!. User needs OrderModel reference and For OrderModel , it needs UserModel object reference. A bidirectional link will be created.
<relation code="User2Orders" generate="true" localized="false" autocreate="true">
<sourceElement type="User" cardinality="one" qualifier="user">
<modifiers read="true" write="true" search="true" optional="false"/>
</sourceElement>
<targetElement type="Order" cardinality="many" qualifier="orders">
<modifiers read="true" write="true" search="true" optional="true" partof="true"/>
</targetElement>
</relation>
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.