What and why it happens
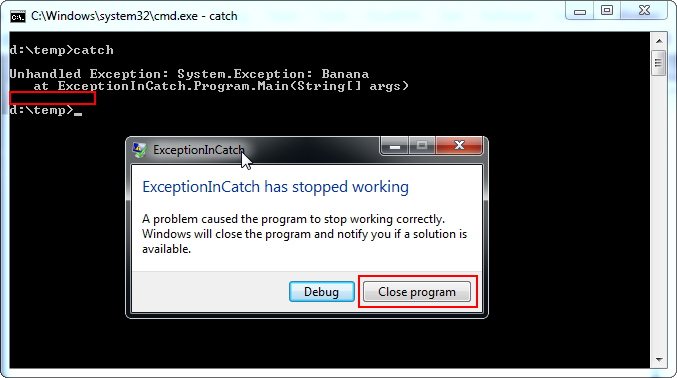
The result depends on what button you click when the program crashes. If you're slow, the Windows Error Reporting (WER) dialog will show "Debug" and "Close program". If you press the "Close program" button, the program is terminated by the operationg system without any chance of writing something else to console.
![Screenshot: close program]()
If you're fast enough to hit the "Cancel" button, then the Windows Error Reporting part will be cancelled and control goes back to your program. It will then write "Carrot" to the Console.
![Screenshot: cancel]()
Therefore, this is not a .NET issue but it's a matter on how Windows reacts to exception dispatching.
How to get control over it
To disable the WER dialog, you can use WerAddExcludedApplication . To get rid of the Debug dialog, you can use SetErrorMode.
Please make yourself familiar with the disadvantages of using those methods. Read Raymond Chen's comments on WerAddExcludedApplication and check whether SetThreadErrorMode might be in favor.
Your code may then look like this:
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace ExceptionInCatch
{
class Program
{
[DllImport("wer.dll", SetLastError = true, CharSet = CharSet.Unicode)]
static extern int WerAddExcludedApplication(String pwzExeName, bool bAllUsers);
[Flags]
public enum ErrorModes : uint
{
SYSTEM_DEFAULT = 0x0,
SEM_FAILCRITICALERRORS = 0x0001,
SEM_NOALIGNMENTFAULTEXCEPT = 0x0004,
SEM_NOGPFAULTERRORBOX = 0x0002,
SEM_NOOPENFILEERRORBOX = 0x8000,
SEM_NONE = SEM_FAILCRITICALERRORS | SEM_NOALIGNMENTFAULTEXCEPT | SEM_NOGPFAULTERRORBOX | SEM_NOOPENFILEERRORBOX
}
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
static extern ErrorModes SetErrorMode(ErrorModes uMode);
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var executableName = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.FriendlyName;
WerAddExcludedApplication(executableName, false);
SetErrorMode(ErrorModes.SEM_NONE);
try
{
throw new Exception("Apple");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception("Banana");
}
finally
{
// This line will now execute
Console.WriteLine("Carrot");
}
}
}
}