Swift 4.2
In my case, if user change the language setting, I have to update 2 things at runtime.
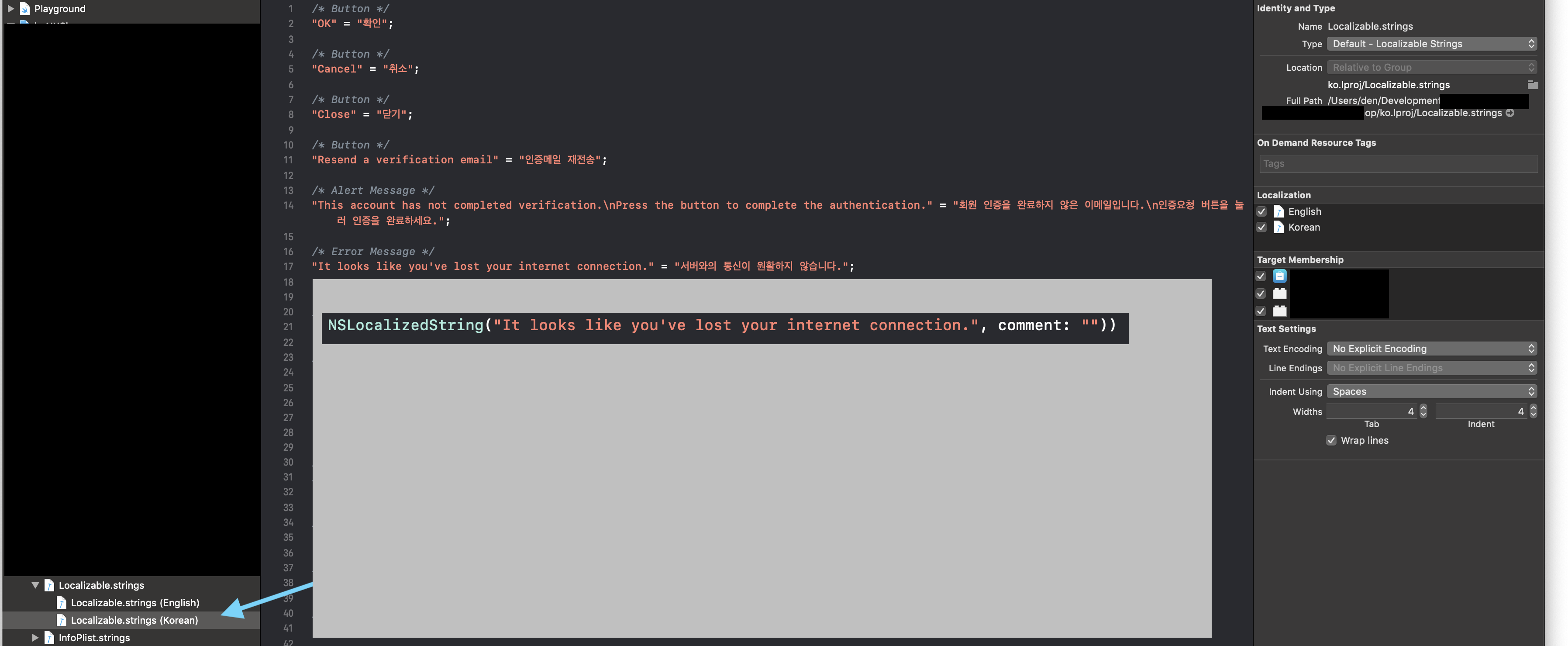
1. Localizable.strings
![Localizable strings]()
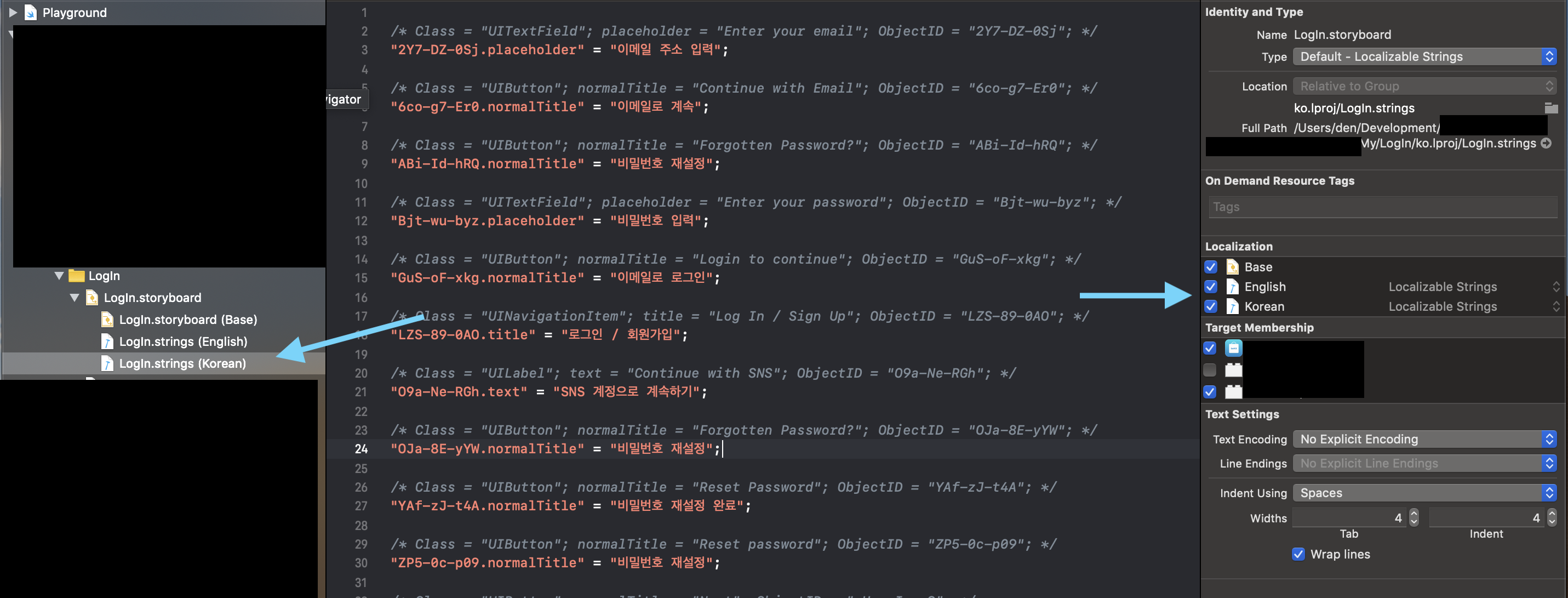
2. Storyboard Localization
![Storyboard localization]()
I make @John Pang code more swifty
BundleExtension.swift
import UIKit
private var bundleKey: UInt8 = 0
final class BundleExtension: Bundle {
override func localizedString(forKey key: String, value: String?, table tableName: String?) -> String {
return (objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &bundleKey) as? Bundle)?.localizedString(forKey: key, value: value, table: tableName) ?? super.localizedString(forKey: key, value: value, table: tableName)
}
}
extension Bundle {
static let once: Void = { object_setClass(Bundle.main, type(of: BundleExtension())) }()
static func set(language: Language) {
Bundle.once
let isLanguageRTL = Locale.characterDirection(forLanguage: language.code) == .rightToLeft
UIView.appearance().semanticContentAttribute = isLanguageRTL == true ? .forceRightToLeft : .forceLeftToRight
UserDefaults.standard.set(isLanguageRTL, forKey: "AppleTe zxtDirection")
UserDefaults.standard.set(isLanguageRTL, forKey: "NSForceRightToLeftWritingDirection")
UserDefaults.standard.set([language.code], forKey: "AppleLanguages")
UserDefaults.standard.synchronize()
guard let path = Bundle.main.path(forResource: language.code, ofType: "lproj") else {
log(.error, "Failed to get a bundle path.")
return
}
objc_setAssociatedObject(Bundle.main, &bundleKey, Bundle(path: path), objc_AssociationPolicy.OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
}
Language.swift
import Foundation
enum Language: Equatable {
case english(English)
case chinese(Chinese)
case korean
case japanese
enum English {
case us
case uk
case australian
case canadian
case indian
}
enum Chinese {
case simplified
case traditional
case hongKong
}
}
extension Language {
var code: String {
switch self {
case .english(let english):
switch english {
case .us: return "en"
case .uk: return "en-GB"
case .australian: return "en-AU"
case .canadian: return "en-CA"
case .indian: return "en-IN"
}
case .chinese(let chinese):
switch chinese {
case .simplified: return "zh-Hans"
case .traditional: return "zh-Hant"
case .hongKong: return "zh-HK"
}
case .korean: return "ko"
case .japanese: return "ja"
}
}
var name: String {
switch self {
case .english(let english):
switch english {
case .us: return "English"
case .uk: return "English (UK)"
case .australian: return "English (Australia)"
case .canadian: return "English (Canada)"
case .indian: return "English (India)"
}
case .chinese(let chinese):
switch chinese {
case .simplified: return "简体中文"
case .traditional: return "繁體中文"
case .hongKong: return "繁體中文 (香港)"
}
case .korean: return "한국어"
case .japanese: return "日本語"
}
}
}
extension Language {
init?(languageCode: String?) {
guard let languageCode = languageCode else { return nil }
switch languageCode {
case "en", "en-US": self = .english(.us)
case "en-GB": self = .english(.uk)
case "en-AU": self = .english(.australian)
case "en-CA": self = .english(.canadian)
case "en-IN": self = .english(.indian)
case "zh-Hans": self = .chinese(.simplified)
case "zh-Hant": self = .chinese(.traditional)
case "zh-HK": self = .chinese(.hongKong)
case "ko": self = .korean
case "ja": self = .japanese
default: return nil
}
}
}
Use like this
var languages: [Language] = [.korean, .english(.us), .english(.uk), .english(.australian), .english(.canadian), .english(.indian),
.chinese(.simplified), .chinese(.traditional), .chinese(.hongKong),
.japanese]
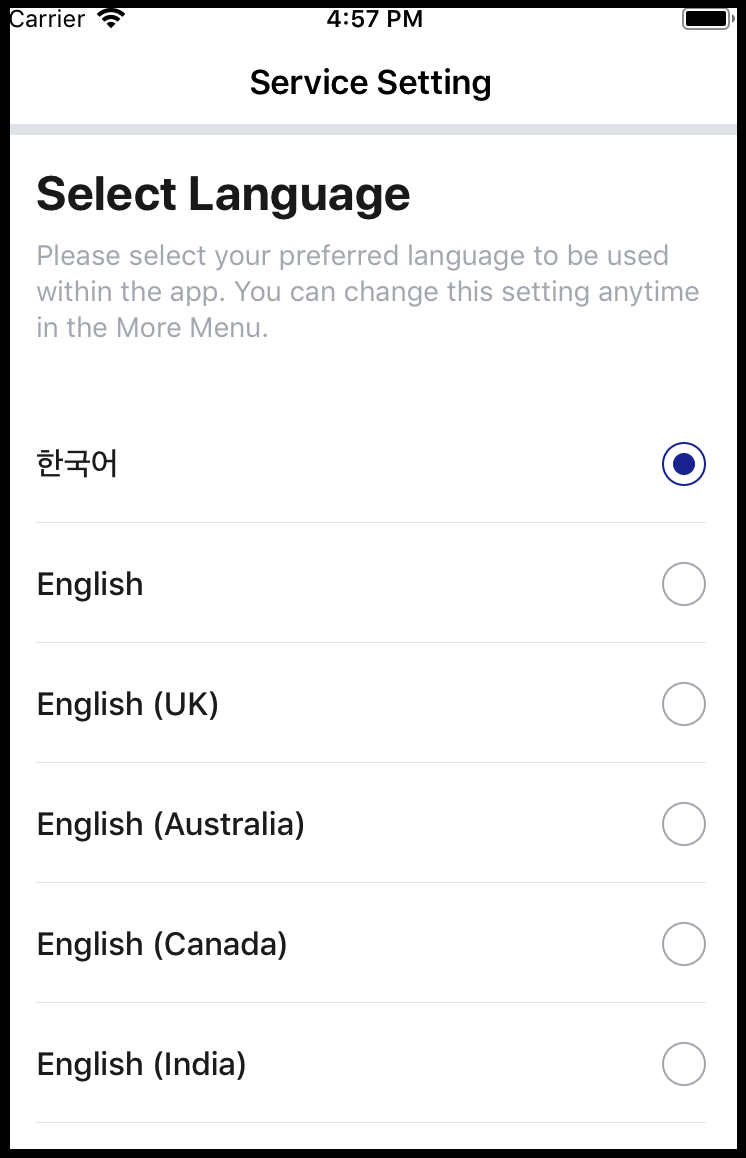
Bundle.set(language: languages[indexPath.row].language)
![Select language screen]()
"Locale.current.languageCode" will always return system setting language.
So we have to use "Locale.preferredLanguages.first". However the return value looks like "ko-US". This is problem ! So I made the LocaleManager to get only the language code.
LocaleManager.swift
import Foundation
struct LocaleManager {
/// "ko-US" → "ko"
static var languageCode: String? {
guard var splits = Locale.preferredLanguages.first?.split(separator: "-"), let first = splits.first else { return nil }
guard 1 < splits.count else { return String(first) }
splits.removeLast()
return String(splits.joined(separator: "-"))
}
static var language: Language? {
return Language(languageCode: languageCode)
}
}
Use like this
guard let languageCode = LocaleManager.languageCode, let title = RemoteConfiguration.shared.logIn?.main?.title?[languageCode] else {
return NSLocalizedString("Welcome!", comment: "")
}
return title