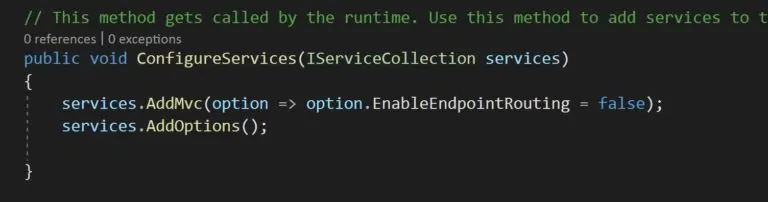
but I need to know what is the proper way to solve it
In general, you should use EnableEndpointRouting instead of UseMvc, and you could refer Update routing startup code for detail steps to enable EnableEndpointRouting.
why Endpoint Routing does not need UseMvc() function.
For UseMvc, it uses the IRouter-based logic and EnableEndpointRouting uses endpoint-based logic. They are following different logic which could be found below:
if (options.Value.EnableEndpointRouting)
{
var mvcEndpointDataSource = app.ApplicationServices
.GetRequiredService<IEnumerable<EndpointDataSource>>()
.OfType<MvcEndpointDataSource>()
.First();
var parameterPolicyFactory = app.ApplicationServices
.GetRequiredService<ParameterPolicyFactory>();
var endpointRouteBuilder = new EndpointRouteBuilder(app);
configureRoutes(endpointRouteBuilder);
foreach (var router in endpointRouteBuilder.Routes)
{
// Only accept Microsoft.AspNetCore.Routing.Route when converting to endpoint
// Sub-types could have additional customization that we can't knowingly convert
if (router is Route route && router.GetType() == typeof(Route))
{
var endpointInfo = new MvcEndpointInfo(
route.Name,
route.RouteTemplate,
route.Defaults,
route.Constraints.ToDictionary(kvp => kvp.Key, kvp => (object)kvp.Value),
route.DataTokens,
parameterPolicyFactory);
mvcEndpointDataSource.ConventionalEndpointInfos.Add(endpointInfo);
}
else
{
throw new InvalidOperationException($"Cannot use '{router.GetType().FullName}' with Endpoint Routing.");
}
}
if (!app.Properties.TryGetValue(EndpointRoutingRegisteredKey, out _))
{
// Matching middleware has not been registered yet
// For back-compat register middleware so an endpoint is matched and then immediately used
app.UseEndpointRouting();
}
return app.UseEndpoint();
}
else
{
var routes = new RouteBuilder(app)
{
DefaultHandler = app.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<MvcRouteHandler>(),
};
configureRoutes(routes);
routes.Routes.Insert(0, AttributeRouting.CreateAttributeMegaRoute(app.ApplicationServices));
return app.UseRouter(routes.Build());
}
For EnableEndpointRouting, it uses EndpointMiddleware to route the request to the endpoints.