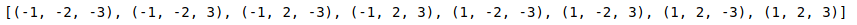I have a list of arrays and I would like to get the cartesian product of the elements in the arrays.
I will use an example to make this more concrete...
itertools.product seems to do the trick but I am stuck in a little detail.
arrays = [(-1,+1), (-2,+2), (-3,+3)];
If I do
cp = list(itertools.product(arrays));
I get
cp = cp0 = [((-1, 1),), ((-2, 2),), ((-3, 3),)]
But what I want to get is
cp1 = [(-1,-2,-3), (-1,-2,+3), (-1,+2,-3), (-1,+2,+3), ..., (+1,+2,-3), (+1,+2,+3)].
I have tried a few different things:
cp = list(itertools.product(itertools.islice(arrays, len(arrays))));
cp = list(itertools.product(iter(arrays, len(arrays))));
They all gave me cp0 instead of cp1.
Any ideas?
Thanks in advance.