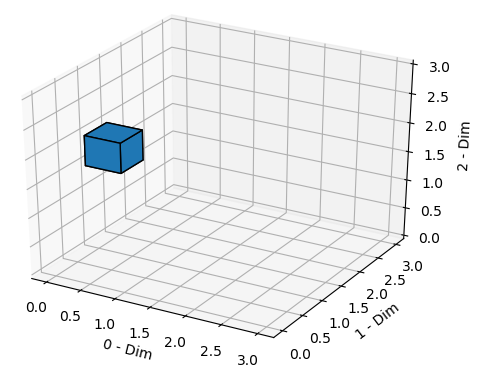
Want to scale the voxel-dimensions with Matplotlib. How can I do this?
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
# Make grid
test2 = np.zeros((6, 6, 6))
# Activate single Voxel
test2[1, 0, 4] = True
ax.voxels(test2, edgecolor="k")
ax.set_xlabel('0 - Dim')
ax.set_ylabel('1 - Dim')
ax.set_zlabel('2 - Dim')
plt.show()
Instead the voxel on position (1,0,4). I want to scale it on (0.5,0,2).