6k views and no answer with code example.
I've worked exactly on this problem so I thought I should bring this back from the dead to help you next person who stumbles upon this;
Marco13's answer was the way to go; using a Quadtree.
(My work is based off of https://github.com/Josephbakulikira/QuadTree-Visualization-with-python--pygame)
I implemented a Quadtree in python, so I could check streets closest to specific addresses on a map database. I think this represents pretty much what the OP wanted to do.
My quadtree takes in lines segments, and points. Which are in my case road segments, and house locations.
I can then query the quadtree at a specific point with a certain radius, to pick road segments close to this point, and get the closest segment.
Here is the code:
quadtree.py:
from shapes import Rectangle, Vector2, Line, Circle
class QuadTree:
"""
Python representation of a QuadTree
"""
def __init__(self, capacity : int, boundary : Rectangle) -> None:
self.capacity : int = capacity
self.boundary : Rectangle = boundary
self.elements = set([])
self.northWest : QuadTree = None
self.northEast : QuadTree = None
self.southWest : QuadTree = None
self.southEast : QuadTree = None
return
@property
def children(self) -> list | bool:
"""
Checker if tree has children.
If yes, returns them in list
"""
if self.northWest != None:
return [self.northWest, self.northEast, self.southWest, self.southEast]
else:
return False
def subdivide(self) -> None:
"""
Divide current tree into quadrants (children)
"""
parent = self.boundary
differencex = (parent.bottomRight.x - parent.topLeft.x) / 2
differencey = (parent.bottomRight.y - parent.topLeft.y) / 2
# Setup children boundaries
boundary_nw = Rectangle(
Vector2(parent.topLeft.x , parent.topLeft.y),
Vector2(parent.bottomRight.x - differencex, parent.bottomRight.y - differencey)
)
boundary_ne = Rectangle(
Vector2(parent.topLeft.x + differencex, parent.topLeft.y),
Vector2(parent.bottomRight.x, parent.bottomRight.y - differencey)
)
boundary_sw = Rectangle(
Vector2(parent.topLeft.x, parent.topLeft.y + differencey),
Vector2(parent.topLeft.x + differencex, parent.bottomRight.y)
)
boundary_se = Rectangle(
Vector2(parent.topLeft.x + differencex, parent.topLeft.y + differencey),
Vector2(parent.bottomRight.x, parent.bottomRight.y)
)
self.northWest = QuadTree(self.capacity, boundary_nw)
self.northEast = QuadTree(self.capacity, boundary_ne)
self.southWest = QuadTree(self.capacity, boundary_sw)
self.southEast = QuadTree(self.capacity, boundary_se)
# Add parent's elements to children
for element in self.elements:
self.insertinchildren(element)
# Clear elements from parent once they are added to children
self.elements = set([])
return
def insert(self, element) -> bool:
"""
Insert element into tree.
If tree is at max capacity, subdivide it, and add elements to children
"""
if self.boundary.containsElement(element) == False:
return False
if len(self.elements) < self.capacity and not self.children:
self.elements.add(element)
return True
else:
if len(self.elements) == self.capacity and not self.children:
if type(element) == Line:
if element in self.elements:
return True
if not self.children:
self.subdivide()
return self.insertinchildren(element)
def insertinchildren(self, element) -> bool:
"""
Insert element into children
(Insert lines everywhere they intersect, while
inserting points(Vectors) only in one quadrant they are in)
"""
if isinstance(element, Line):
self.northWest.insert(element)
self.northEast.insert(element)
self.southWest.insert(element)
self.southEast.insert(element)
return True
else:
if not self.northWest.insert(element):
if not self.northEast.insert(element):
if not self.southWest.insert(element):
if not self.southEast.insert(element):
return False
return True
def query(self, _range : Rectangle | Circle) -> set:
"""
Use a circle or rectangle to query the tree for
elements in range
"""
elements_in_range = set([])
if _range.intersects(self.boundary):
if self.children:
elements_in_range.update(self.northWest.query(_range))
elements_in_range.update(self.northEast.query(_range))
elements_in_range.update(self.southWest.query(_range))
elements_in_range.update(self.southEast.query(_range))
else:
for element in self.elements:
if _range.containsElement(element):
elements_in_range.add(element)
return elements_in_range
shapes.py
import numpy as np
class Vector2(np.ndarray):
"""
Numpy array subclass to represent a 2D vector
"""
def __new__(cls, x, y) -> np.ndarray:
return np.array([x, y]).view(cls)
@property
def x(self) -> float:
return self[0]
@property
def y(self) -> float:
return self[1]
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return id(self)
def __eq__(self, other) -> bool:
if not isinstance(other, Vector2):
return False
return np.array_equal(self, other)
class Line:
"""
Representation of a line segment
"""
def __init__(self, point1 : Vector2, point2 : Vector2) -> None:
self.a = point1
self.b = point2
return
def __str__(self) -> str:
return f"Line({self.a}, {self.b})"
def distancetoPoint(self, p : Vector2) -> float:
"""
Get the shortest distance between point p and the line segment
"""
# Distance between the closest point and the point p
return np.linalg.norm(self.closestPoint(p) - p)
def closestPoint(self, p : Vector2) -> float:
"""
Get the closest point on the line segment from point p
"""
a = self.a
b = self.b
cp = None # Closest point
ab = b - a
ap = p - a
proj = np.dot(ap, ab)
abLenSq = ab[0]**2 + ab[1]**2
normalizedProj = proj / abLenSq
if normalizedProj <= 0:
cp = a
elif normalizedProj >= 1:
cp = b
else:
cp = a + normalizedProj * ab
return cp
def onSegment(self, p, q, r) -> bool:
"""
Given three collinear points p, q, r, the function checks if
point q lies on line segment 'pr'
"""
if ( (q.x <= max(p.x, r.x)) and (q.x >= min(p.x, r.x)) and
(q.y <= max(p.y, r.y)) and (q.y >= min(p.y, r.y))):
return True
return False
def orientation(self, p, q, r) -> int:
"""
To find the orientation of an ordered triplet (p,q,r)
function returns the following values:
0 : Collinear points
1 : Clockwise points
2 : Counterclockwise
See https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/orientation-3-ordered-points/amp/
for details of below formula.
"""
val = (float(q.y - p.y) * (r.x - q.x)) - (float(q.x - p.x) * (r.y - q.y))
if (val > 0):
# Clockwise orientation
return 1
elif (val < 0):
# Counterclockwise orientation
return 2
else:
# Collinear orientation
return 0
def intersects(self, p1 : Vector2, p2 : Vector2) -> bool:
"""
Check if current line intersects with another line
made of point1 and point2
"""
# Find the 4 orientations required for
# the general and special cases
o1 = self.orientation(self.a, self.b, p1)
o2 = self.orientation(self.a, self.b, p2)
o3 = self.orientation(p1, p2, self.a)
o4 = self.orientation(p1, p2, self.b)
# General case
if ((o1 != o2) and (o3 != o4)):
return True
# _____________ Special Cases _____________
# self.a , self.b and p1 are collinear and p1 lies on segment p1q1
if ((o1 == 0) and self.onSegment(self.a, p1, self.b)):
return True
# self.a , self.b and p2 are collinear and p2 lies on segment p1q1
if ((o2 == 0) and self.onSegment(self.a, p2, self.b)):
return True
# p1 , p2 and self.a are collinear and self.a lies on segment p2q2
if ((o3 == 0) and self.onSegment(p1, self.a, p2)):
return True
# p1 , p2 and self.b are collinear and self.b lies on segment p2q2
if ((o4 == 0) and self.onSegment(p1, self.b, p2)):
return True
# If none of the cases
return False
class Rectangle:
"""
Rectangle used as boundaries for the QuadTree
or as a query range for the QuadTree
"""
def __init__(self, topLeft : Vector2, bottomRight : Vector2) -> None:
self.topLeft = topLeft
self.bottomRight = bottomRight
self.topRight = Vector2(self.bottomRight.x, self.topLeft.y)
self.bottomLeft = Vector2(self.topLeft.x, self.bottomRight.y)
self.center = (self.topLeft + self.bottomRight) / 2
self.top = Line(self.topLeft, Vector2(self.bottomRight.x, self.topLeft.y))
self.bottom = Line(Vector2(self.topLeft.x, self.bottomRight.y), self.bottomRight)
self.left = Line(self.topLeft, Vector2(self.topLeft.x, self.bottomRight.y))
self.right = Line(Vector2(self.bottomRight.x, self.topLeft.y), self.bottomRight)
return
def __str__(self) -> str:
return f"Rectangle({self.topLeft}, {self.bottomRight})"
def containsElement(self, element : Vector2 | Line) -> bool:
"""
Checks if the element is contained by this rectangle
"""
if isinstance(element, Line):
return self.containsLine(element)
x, y = element
bx , by = self.topLeft
cx, cy = self.bottomRight
if x >= bx and x <= cx and y >= by and y <= cy:
return True
else:
return False
def containsLine(self, line : Line) -> bool:
"""
Checks if the line goes through this rectangle
"""
# Check if any end of the line is inside the rectangle
if self.containsElement(line.a) or self.containsElement(line.b):
return True
# Check if line intersects with any side of the rectangle
else:
if not line.intersects(self.top.a, self.top.b):
if not line.intersects(self.bottom.a, self.bottom.b):
if not line.intersects(self.left.a, self.left.b):
if not line.intersects(self.right.a, self.right.b):
return False
return True
def intersects(self, other : 'Rectangle') -> bool:
"""
Check if this rectangle intersects with another rectangle
ie. if any of the sides of the rectangle crosses another rectangle
"""
return not (self.bottomRight.x < other.topLeft.x
or self.topLeft.x > other.bottomRight.x
or self.bottomRight.y < other.topLeft.y
or self.topLeft.y > other.bottomRight.y)
class Circle:
"""
Circle used as range to query the QuadTree
"""
def __init__(self, center : Vector2, radius : float) -> None:
self.center = center
self.radius = radius
return
def __str__(self) -> str:
return f"Circle({self.center}, r{self.radius})"
def containsElement(self, element : Vector2 | Line) -> bool:
"""
Checks if the element is contained by this circle
"""
if isinstance(element, Line):
return self.containsLine(element)
dist = np.linalg.norm(self.center - element)
if dist <= self.radius:
return True
else:
return False
def containsLine(self, line : Line) -> bool:
"""
Checks if the line goes through this circle
"""
if line.distancetoPoint(self.center) <= self.radius:
return True
else:
return False
def intersects(self, rectangle : Rectangle) -> bool:
"""
Check if this circle intersects with a rectangle
"""
# There are only two cases where a circle and a rectangle can intersect:
# 1. The circle center is inside the rectangle
if not rectangle.containsElement(self.center):
# 2. The circle intersects with one of the rectangle's sides
if not self.containsLine(rectangle.top):
if not self.containsLine(rectangle.bottom):
if not self.containsLine(rectangle.left):
if not self.containsLine(rectangle.right):
return False
return True
main.py
from quadtree import QuadTree
from shapes import Rectangle, Circle, Vector2, Line
# Setup lines with Overpass nodes
node0 = Vector2(107.1360616, 46.1032011)
node1 = Vector2(107.13563750000003, 46.102939)
node2 = Vector2(107.13538800000003, 46.1028447)
node3 = Vector2(107.13493060000002, 46.1027272)
node4 = Vector2(107.13318809999998, 46.1021657)
node5 = Vector2(107.13255700000002, 46.1019075)
node6 = Vector2(107.1316817, 46.1014684)
node7 = Vector2(107.13088449999998, 46.1011467)
node8 = Vector2(107.1304002, 46.1010027)
node9 = Vector2(107.1299055, 46.1009219)
node10 = Vector2(107.12915320000002, 46.1008729)
node11 = Vector2(107.12877689999999, 46.1008901)
node12 = Vector2(107.12828999999999, 46.10097)
node13 = Vector2(107.1274209, 46.1012472)
node14 = Vector2(107.1270212, 46.1014094)
node15 = Vector2(107.1265209, 46.101732)
node16 = Vector2(107.12579249999999, 46.1022694)
node17 = Vector2(107.1256219, 46.1024435)
node18 = Vector2(107.12546250000003, 46.1026809)
node19 = Vector2(107.12500690000002, 46.1034946)
nodes = [node0, node1, node2, node3, node4, node5, node6, node7, node8, node9,
node10, node11, node12, node13, node14, node15, node16, node17, node18, node19]
lines = []
for i in range(len(nodes)-1):
lines.append(Line(nodes[i], nodes[i+1]))
# Setup points
house0 = Vector2(107.13595197486893, 46.10285045021604)
house1 = Vector2(107.1300706177878, 46.101115083412374)
house2 = Vector2(107.13043003379954, 46.100917943095524)
house3 = Vector2(107.13046758472615, 46.101234111186926)
house4 = Vector2(107.13071434795808, 46.10100721426972)
house5 = Vector2(107.13108449280605, 46.10108904605243)
house6 = Vector2(107.12480471447458, 46.10391049893959)
house7 = Vector2(107.12635081112013, 46.10232085692584)
houses = [house0, house1, house2, house3, house4, house5, house6, house7]
# Setup quadtree
tree = QuadTree(2, Rectangle(Vector2(107.12383, 46.09690), Vector2(107.13709, 46.10700)))
for l in lines:
tree.insert(l)
for h in houses:
tree.insert(h)
# Setup query
queryAT = Vector2(107.12739, 46.10358)
radQuery = Circle(queryAT, 0.0022)
found_elements = tree.query(radQuery)
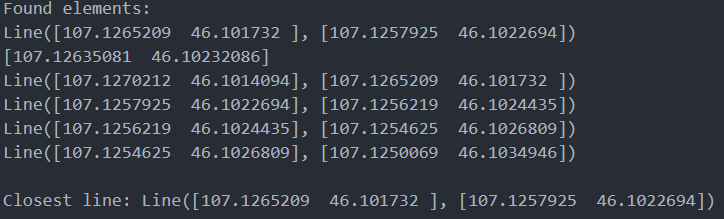
print("Found elements:")
for element in found_elements:
print(element)
# Find closest line
shortest_dist = 999999
closest_line = None
for element in found_elements:
if isinstance(element, Line):
dist = element.distancetoPoint(queryAT)
if dist < shortest_dist:
shortest_dist = dist
closest_line = element
print("\nClosest line: " + str(closest_line))
# ---------- Represent everything in a graph ------------
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_xlim(tree.boundary.topLeft.x, tree.boundary.bottomRight.x)
ax.set_ylim(tree.boundary.topLeft.y, tree.boundary.bottomRight.y)
def plot_tree(ax, quadtree):
"""
Traverse the quadtree recursively and
plot the boundaries and elements of each node
"""
if quadtree.children:
for child in quadtree.children:
plot_tree(ax, child)
else:
ax.add_patch(patches.Rectangle((quadtree.boundary.topLeft.x, quadtree.boundary.topLeft.y), quadtree.boundary.bottomRight.x-quadtree.boundary.topLeft.x, quadtree.boundary.bottomRight.y - quadtree.boundary.topLeft.y, fill=False))
for element in quadtree.elements:
clr = 'black'
if element in found_elements:
clr = 'magenta'
if element is closest_line:
clr = 'red'
if isinstance(element, Line):
ax.plot([element.a.x, element.b.x], [element.a.y, element.b.y], color=clr)
#plot end segments as dots:
ax.plot(element.a.x, element.a.y, 'o', color=clr)
ax.plot(element.b.x, element.b.y, 'o', color=clr)
elif isinstance(element, Vector2):
ax.plot(element.x, element.y, 'go')
return
plot_tree(ax, tree)
# Add query circle to plot
ax.add_patch(patches.Circle((queryAT.x, queryAT.y), radQuery.radius, fill=False, color='orange'))
# add circle center to plot
ax.plot(queryAT.x, queryAT.y, 'o', color='orange')
ax.set_box_aspect(1) # make the plot square
plt.show()
So in main.py I use coordinates points and setup a Quadtree of an area of approx. 1km square with only one street made of several line segments.
I then query a specific spot (107.12739, 46.10358) lon,lat , at a distance of 0.0022 = around 170meters
This gives me the results:
![enter image description here]()
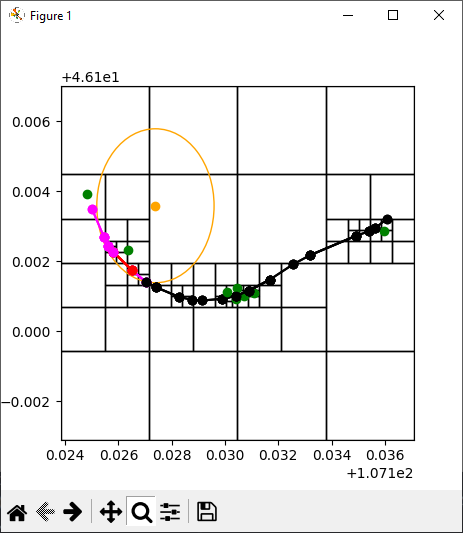
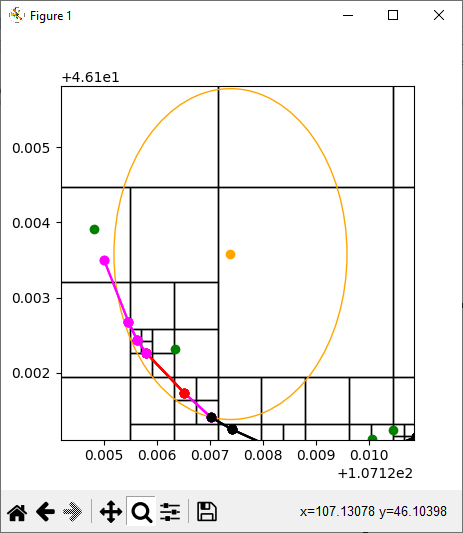
Visualization in matplotlib:
Orange is the query circle
Magenta are the segments found by the query
The red line is the closest line
![enter image description here]()
![enter image description here]()
Is it really more efficient for 1000 segments? I don't know. Anyway, there you go.