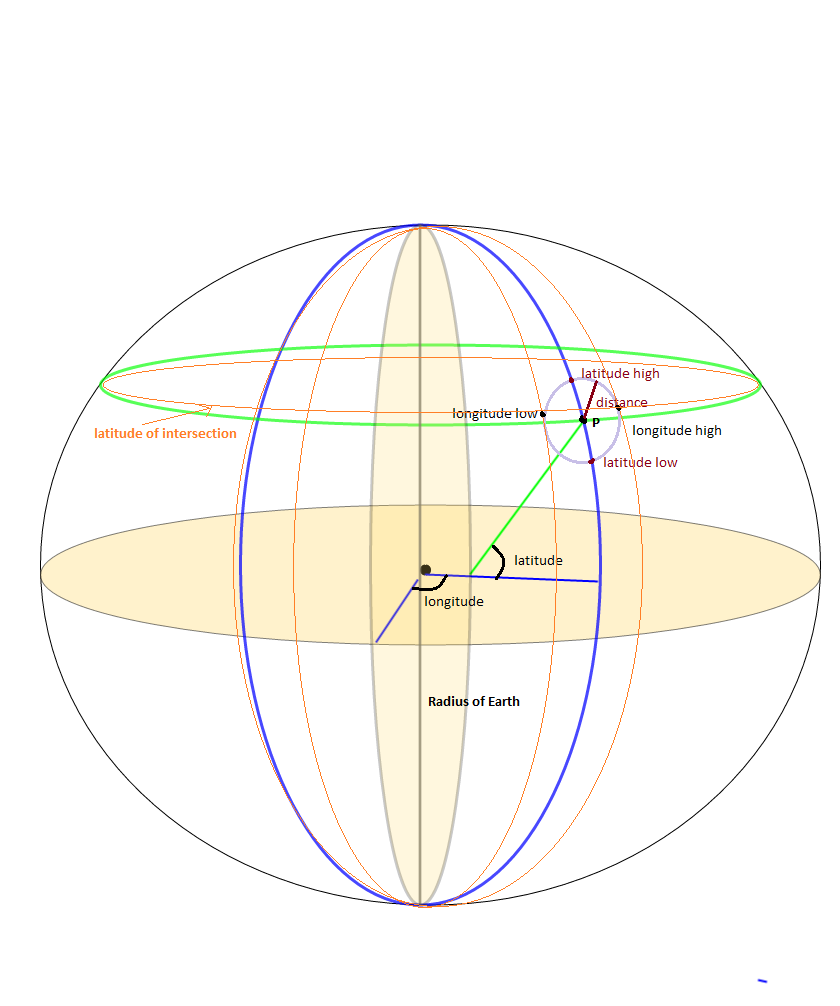
I was working on the bounding box problem as a side issue to finding all the points within SrcRad radius of a static LAT, LONG point. There have been quite a few calculations that use
maxLon = $lon + rad2deg($rad/$R/cos(deg2rad($lat)));
minLon = $lon - rad2deg($rad/$R/cos(deg2rad($lat)));
to calculate the longitude bounds, but I found this to not give all the answers that were needed. Because what you really want to do is
(SrcRad/RadEarth)/cos(deg2rad(lat))
I know, I know the answer should be the same, but I found that it wasn't. It appeared that by not making sure I was doing the (SRCrad/RadEarth) First and then dividing by the Cos part I was leaving out some location points.
After you get all your bounding box points, if you have a function that calculates the Point to Point Distance given lat, long it is easy to only get those points that are a certain distance radius from the fixed point. Here is what I did.
I know it took a few extra steps but it helped me
-- GLOBAL Constants
gc_pi CONSTANT REAL := 3.14159265359; -- Pi
-- Conversion Factor Constants
gc_rad_to_degs CONSTANT NUMBER := 180/gc_pi; -- Conversion for Radians to Degrees 180/pi
gc_deg_to_rads CONSTANT NUMBER := gc_pi/180; --Conversion of Degrees to Radians
lv_stat_lat -- The static latitude point that I am searching from
lv_stat_long -- The static longitude point that I am searching from
-- Angular radius ratio in radians
lv_ang_radius := lv_search_radius / lv_earth_radius;
lv_bb_maxlat := lv_stat_lat + (gc_rad_to_deg * lv_ang_radius);
lv_bb_minlat := lv_stat_lat - (gc_rad_to_deg * lv_ang_radius);
--Here's the tricky part, accounting for the Longitude getting smaller as we move up the latitiude scale
-- I seperated the parts of the equation to make it easier to debug and understand
-- I may not be a smart man but I know what the right answer is... :-)
lv_int_calc := gc_deg_to_rads * lv_stat_lat;
lv_int_calc := COS(lv_int_calc);
lv_int_calc := lv_ang_radius/lv_int_calc;
lv_int_calc := gc_rad_to_degs*lv_int_calc;
lv_bb_maxlong := lv_stat_long + lv_int_calc;
lv_bb_minlong := lv_stat_long - lv_int_calc;
-- Now select the values from your location datatable
SELECT * FROM (
SELECT cityaliasname, city, state, zipcode, latitude, longitude,
-- The actual distance in miles
spherecos_pnttopntdist(lv_stat_lat, lv_stat_long, latitude, longitude, 'M') as miles_dist
FROM Location_Table
WHERE latitude between lv_bb_minlat AND lv_bb_maxlat
AND longitude between lv_bb_minlong and lv_bb_maxlong)
WHERE miles_dist <= lv_limit_distance_miles
order by miles_dist
;