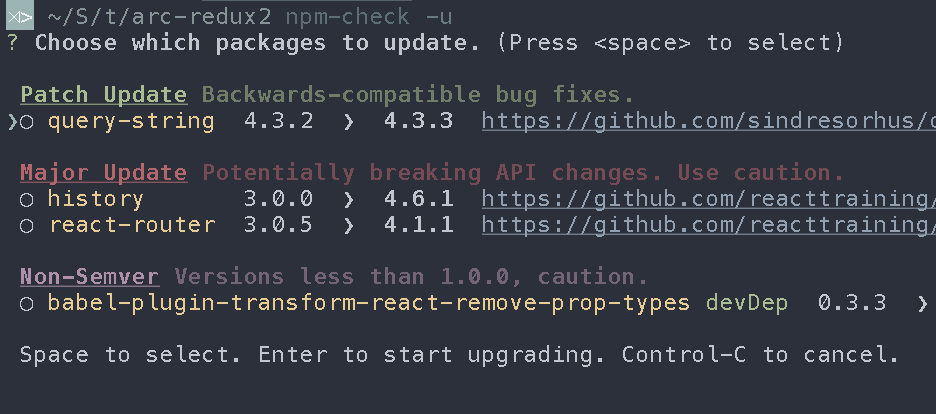
The following code (which was accepted) wrote me something like "it takes too long blah-blah" and did nothing. Probably using the global flag was the problem, idk.
npm i -g npm-check-updates
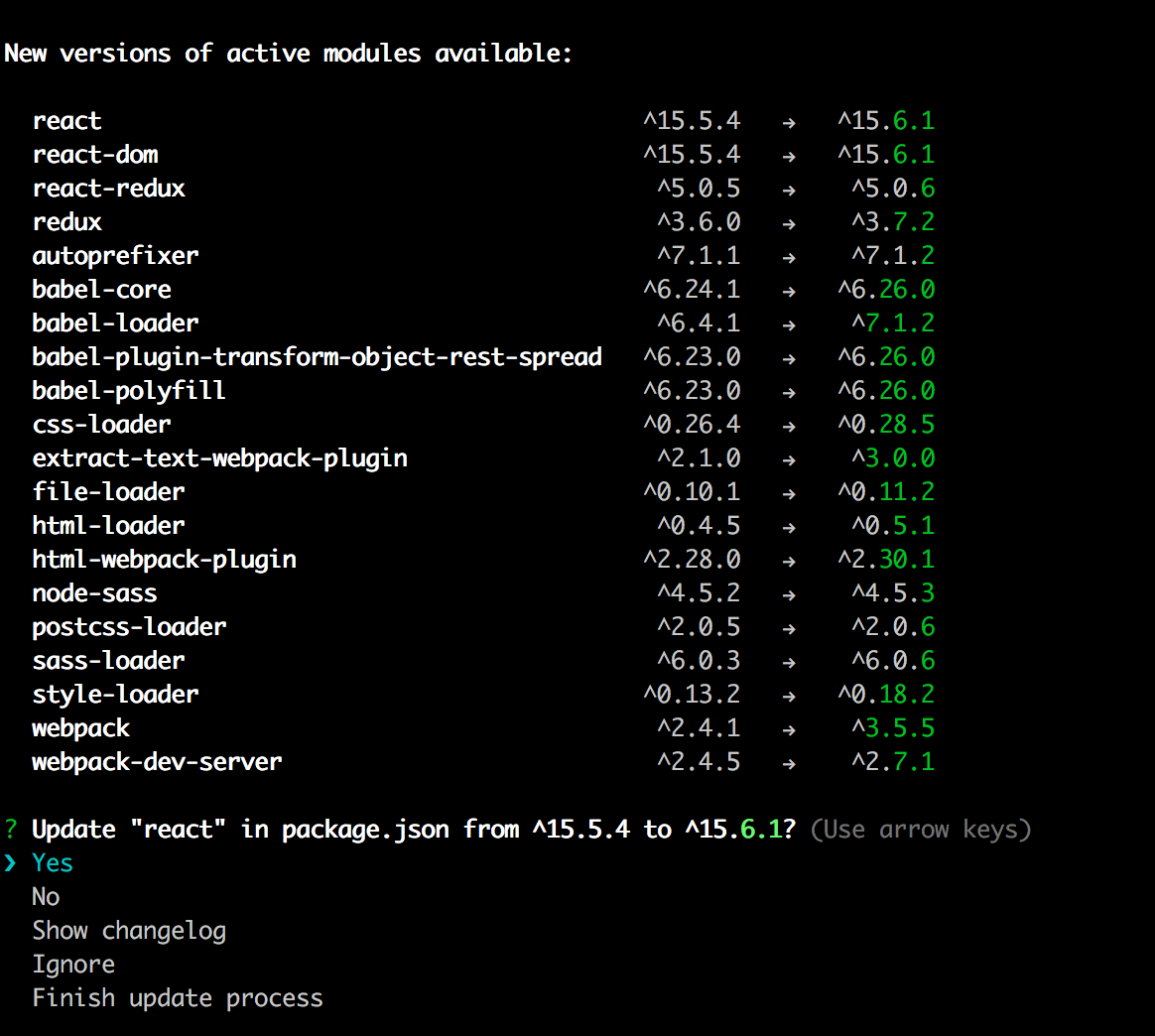
ncu -u
npm install
I decided to use my text editor and follow a semi-manual approach instead.
I copied a list like this (just a lot longer) from the dev dependencies of my package.json to the notepad++ text editor:
"browserify": "10.2.6",
"expect.js": "^0.3.1",
"karma": "^0.13.22",
"karma-browserify": "^5.2.0",
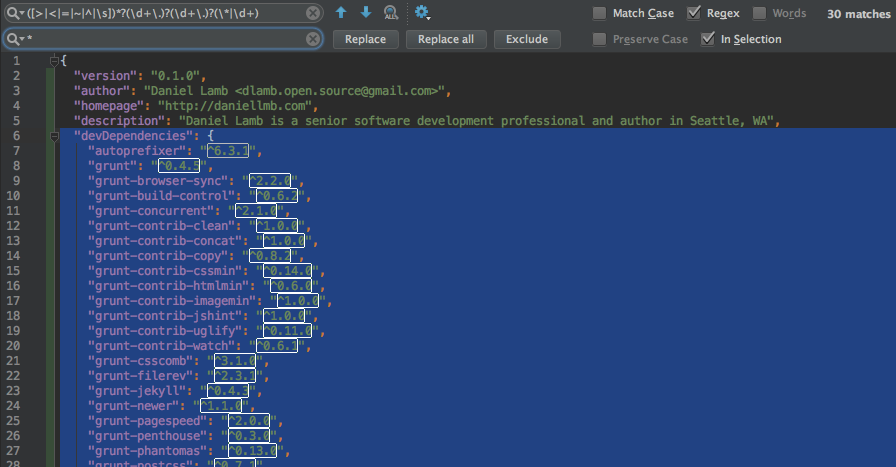
I set the search mode to regular expression, used the ^\s*"([^"]+)".*$ pattern to get the package name and replaced it with npm uninstall \1 --save-dev \nnpm install \1 --save-dev. Clicked on "replace all". The otput was this:
npm uninstall browserify --save-dev
npm install browserify --save-dev
npm uninstall expect.js --save-dev
npm install expect.js --save-dev
npm uninstall karma --save-dev
npm install karma --save-dev
npm uninstall karma-browserify --save-dev
npm install karma-browserify --save-dev
I copied it back to bash and hit enter. Everything was upgraded and working fine. That's all.
"browserify": "^16.1.0",
"expect.js": "^0.3.1",
"karma": "^2.0.0",
"karma-browserify": "^5.2.0",
I don't think it is a big deal, since you have to do it only every now and then, but you can easily write a script, which parses the package.json and upgrades your packages. I think it is better this way, because you can edit your list if you need something special, for example keeping the current version of a lib.

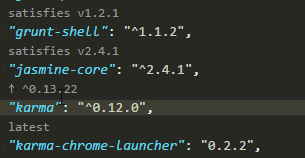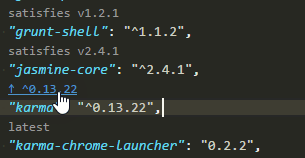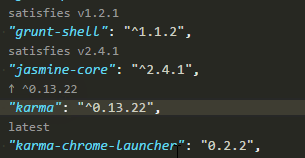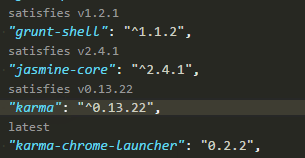
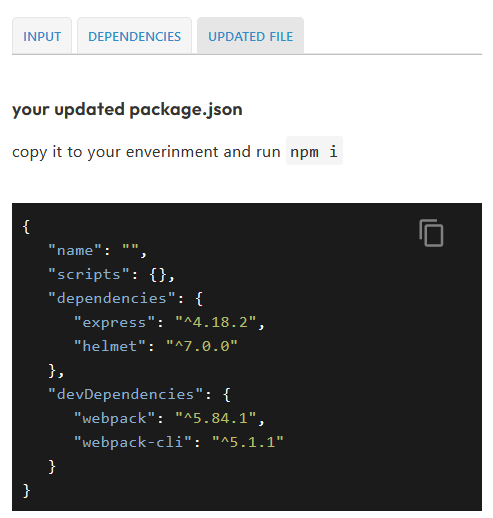
npm outdated | sed '1d; s/ .*/@latest/' | xargs npm i --save– Perlieyarnyou can update your package.json using this command:yarn add bootstrap@latest mongoose@latest next@latest next-auth@latest react@latest react-bootstrap@latest react-dom@latest– Thimbleful