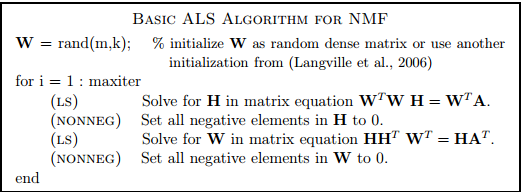
Using nonnegative least squares in this algo as opposed to clipping off negative values would obviously be better in this algorithm, but in general I would not recommend this basic ALS/ANNLS method as it has bad convergence properties (it often fluctuates or can even show divergence) - a minimal Matlab implementation of a better method, the accelerated-Hierarchical Alternating Least Squares method for NMF (of Cichocki et al.), which is currently one of the fastest methods is shown here (code by Nicolas Gillis) :
% Accelerated hierarchical alternating least squares (HALS) algorithm of
% Cichocki et al.
%
% See N. Gillis and F. Glineur, "Accelerated Multiplicative Updates and
% Hierarchical ALS Algorithms for Nonnegative Matrix Factorization”,
% Neural Computation 24 (4), pp. 1085-1105, 2012.
% See http://sites.google.com/site/nicolasgillis/
%
% [U,V,e,t] = HALSacc(M,U,V,alpha,delta,maxiter,timelimit)
%
% Input.
% M : (m x n) matrix to factorize
% (U,V) : initial matrices of dimensions (m x r) and (r x n)
% alpha : nonnegative parameter of the accelerated method
% (alpha=0.5 seems to work well)
% delta : parameter to stop inner iterations when they become
% inneffective (delta=0.1 seems to work well).
% maxiter : maximum number of iterations
% timelimit : maximum time alloted to the algorithm
%
% Output.
% (U,V) : nonnegative matrices s.t. UV approximate M
% (e,t) : error and time after each iteration,
% can be displayed with plot(t,e)
%
% Remark. With alpha = 0, it reduces to the original HALS algorithm.
function [U,V,e,t] = HALSacc(M,U,V,alpha,delta,maxiter,timelimit)
% Initialization
etime = cputime; nM = norm(M,'fro')^2;
[m,n] = size(M); [m,r] = size(U);
a = 0; e = []; t = []; iter = 0;
if nargin <= 3, alpha = 0.5; end
if nargin <= 4, delta = 0.1; end
if nargin <= 5, maxiter = 100; end
if nargin <= 6, timelimit = 60; end
% Scaling, p. 72 of the thesis
eit1 = cputime; A = M*V'; B = V*V'; eit1 = cputime-eit1; j = 0;
scaling = sum(sum(A.*U))/sum(sum( B.*(U'*U) )); U = U*scaling;
% Main loop
while iter <= maxiter && cputime-etime <= timelimit
% Update of U
if j == 1, % Do not recompute A and B at first pass
% Use actual computational time instead of estimates rhoU
eit1 = cputime; A = M*V'; B = V*V'; eit1 = cputime-eit1;
end
j = 1; eit2 = cputime; eps = 1; eps0 = 1;
U = HALSupdt(U',B',A',eit1,alpha,delta); U = U';
% Update of V
eit1 = cputime; A = (U'*M); B = (U'*U); eit1 = cputime-eit1;
eit2 = cputime; eps = 1; eps0 = 1;
V = HALSupdt(V,B,A,eit1,alpha,delta);
% Evaluation of the error e at time t
if nargout >= 3
cnT = cputime;
e = [e sqrt( (nM-2*sum(sum(V.*A))+ sum(sum(B.*(V*V')))) )];
etime = etime+(cputime-cnT);
t = [t cputime-etime];
end
iter = iter + 1; j = 1;
end
% Update of V <- HALS(M,U,V)
% i.e., optimizing min_{V >= 0} ||M-UV||_F^2
% with an exact block-coordinate descent scheme
function V = HALSupdt(V,UtU,UtM,eit1,alpha,delta)
[r,n] = size(V);
eit2 = cputime; % Use actual computational time instead of estimates rhoU
cnt = 1; % Enter the loop at least once
eps = 1; eps0 = 1; eit3 = 0;
while cnt == 1 || (cputime-eit2 < (eit1+eit3)*alpha && eps >= (delta)^2*eps0)
nodelta = 0; if cnt == 1, eit3 = cputime; end
for k = 1 : r
deltaV = max((UtM(k,:)-UtU(k,:)*V)/UtU(k,k),-V(k,:));
V(k,:) = V(k,:) + deltaV;
nodelta = nodelta + deltaV*deltaV'; % used to compute norm(V0-V,'fro')^2;
if V(k,:) == 0, V(k,:) = 1e-16*max(V(:)); end % safety procedure
end
if cnt == 1
eps0 = nodelta;
eit3 = cputime-eit3;
end
eps = nodelta; cnt = 0;
end
For full code and comparison to other methods, see
https://sites.google.com/site/nicolasgillis/code
(section Accelerated MU and HALS algorithms for NMF)
and
N. Gillis and F. Glineur, "Accelerated Multiplicative Updates and Hierarchical ALS Algorithms for Nonnegative Matrix Factorization”, Neural Computation 24 (4), pp. 1085-1105, 2012.