Factory method:
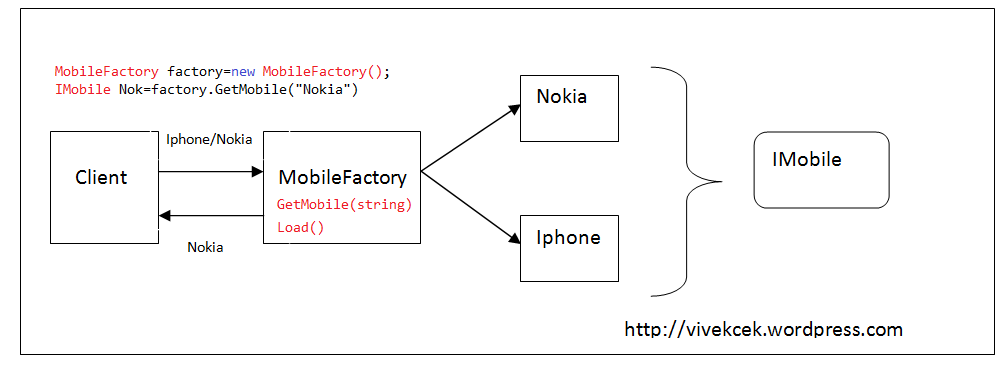
hey everyone. I am looking for the difference between simple factory and factory method.. I know the structural difference(images above), but I cant understand difference in use cases. for example, this is the explanation for factory method:
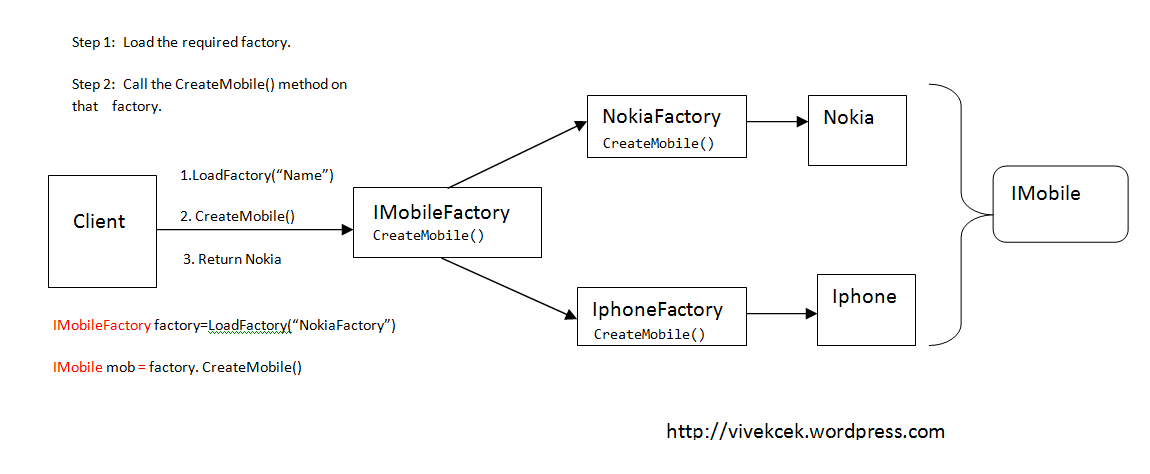
In Factory Method pattern we will introduce a new interface called ‘IMobileFactory’ and two concrete implementation’s ‘NokiaFactory’ and ‘IphoneFactory’. These concrete classes control the object creation.
In my example the client want a Nokia object. So the steps are given below.
1.The client will load a reference to ‘NokiaFactory’. But Client won’t refer the ‘NokiaFactory’ class directly like the Simple Factory pattern. The client refers the concrete implementation through an interface ‘IMobileFactory’.
2.Then the Client call the ‘CreateMobile()’ method that will return an object of type ‘IMobile’.
3.Here we have to inform the client the concrete implementation to be used through some configuration or parameters.
I can't understand the first step:
But Client won’t refer the ‘NokiaFactory’ class directly like the Simple Factory pattern. The client refers the concrete implementation through an interface ‘IMobileFactory’.
so client writes something like this:
IMobileFactory factory = LoadFactory("NokiaFactory");
so why is that useful and better? what's the benefit? why shouldn't I just write this:
NokiaFactory factory = new NokiaFactory();
or what about that:
IMobileFactory factory = new NokiaFactory();

IMobileFactoryinstance during the constructor call. Either way, the goal is to avoid directly referencing concrete classes and use interfaces. Using an interface will make your code more flexible for testing / new use cases because it is not coupled to a single implementation. – Versify