From the documentation, after modifying the daemon.json (adding "live-restore": true) you need to :
Restart the Docker daemon. On Linux, you can avoid a restart (and avoid any downtime for your containers) by reloading the Docker daemon. If you use systemd, then use the command systemctl reload docker. Otherwise, send a SIGHUP signal to the dockerd process.
You can also do this but it's not recommended :
If you prefer, you can start the dockerd process manually with the --live-restore flag. This approach is not recommended because it does not set up the environment that systemd or another process manager would use when starting the Docker process. This can cause unexpected behavior.
It seems that you had not done this step. You said that you've made the modification to the daemon.json and directly started a container and then stopped the dockerd.
In order to make the Live Restore functionality work follow all steps in the right order :
- Modify the
daemon.json by adding "live-restore": true
Reload the Docker daemon with the command :
sudo systemctl reload docker
Then try the functionality with your example (firing up a container and making the daemon unavailable).
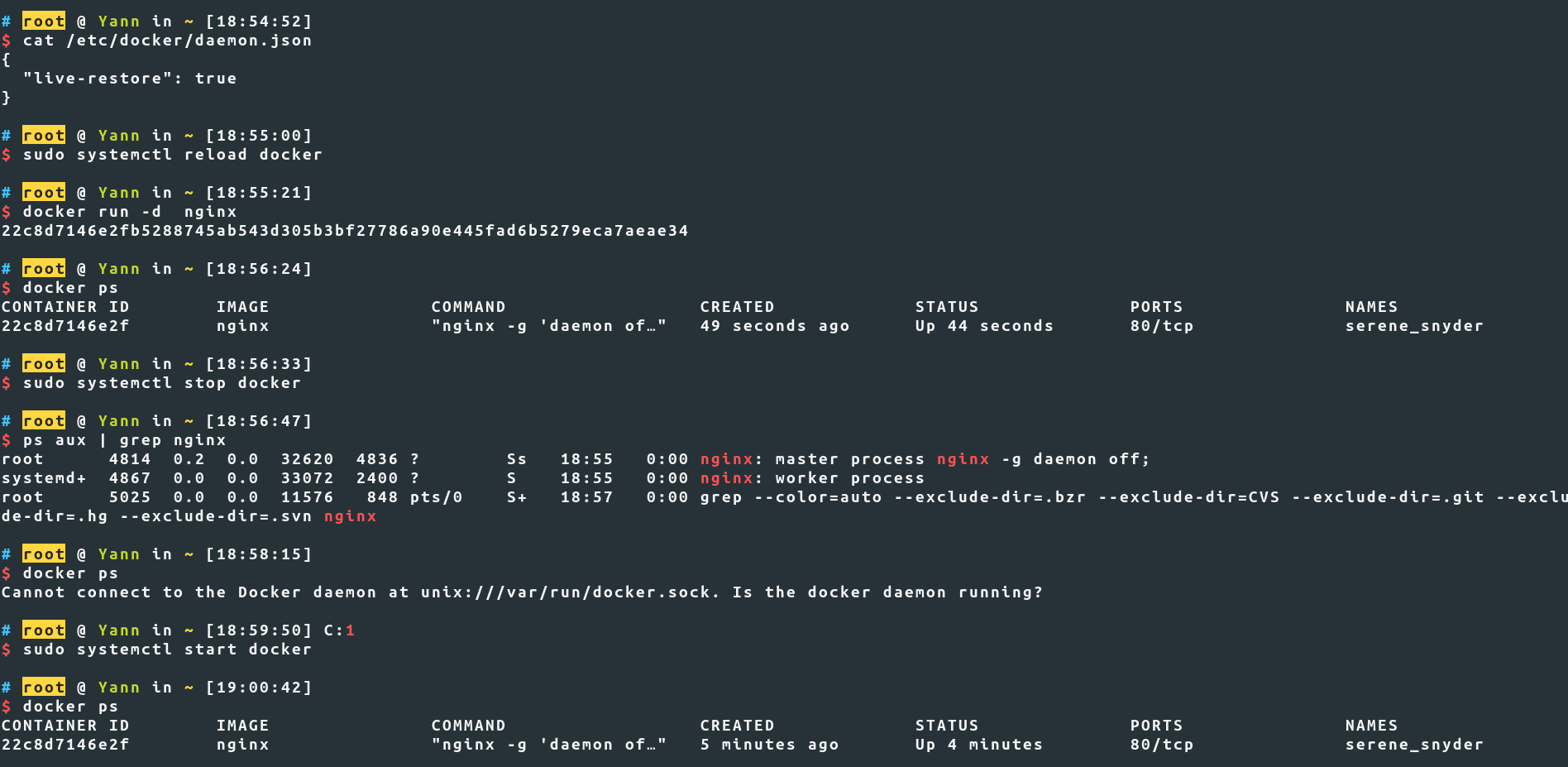
I've tested and it works if you follow the steps in order :
![LiveRestore]()
Tested with Docker version 19.03.2, build 6a30dfc and Ubuntu 19.10 (Eoan Ermine)
You've installed Docker via snap : snap.docker.dockerd.service
Unfortunately, it's not recommended since snap model is not fully compatible with Docker. Furthermore, docker-snap is no longer maintained by Docker, Inc. Users encounters some issues when they installed Docker via snap see 1 2
You should delete the snap Docker installation to avoid any potential overlapping installation issues via this command :
sudo snap remove docker --purge
Then install Docker with the official way and after that try the Live Restore functionality by following the above steps.
Also be careful when restarting the daemon the documentation says that :
Live restore upon restart
The live restore option only works to restore containers if the daemon options, such as bridge IP addresses and graph driver, did not change. If any of these daemon-level configuration options have changed, the live restore may not work and you may need to manually stop the containers.
Also about downtime :
Impact of live restore on running containers
If the daemon is down for a long time, running containers may fill up the FIFO log the daemon normally reads. A full log blocks containers from logging more data. The default buffer size is 64K. If the buffers fill, you must restart the Docker daemon to flush them.
On Linux, you can modify the kernel’s buffer size by changing /proc/sys/fs/pipe-max-size.