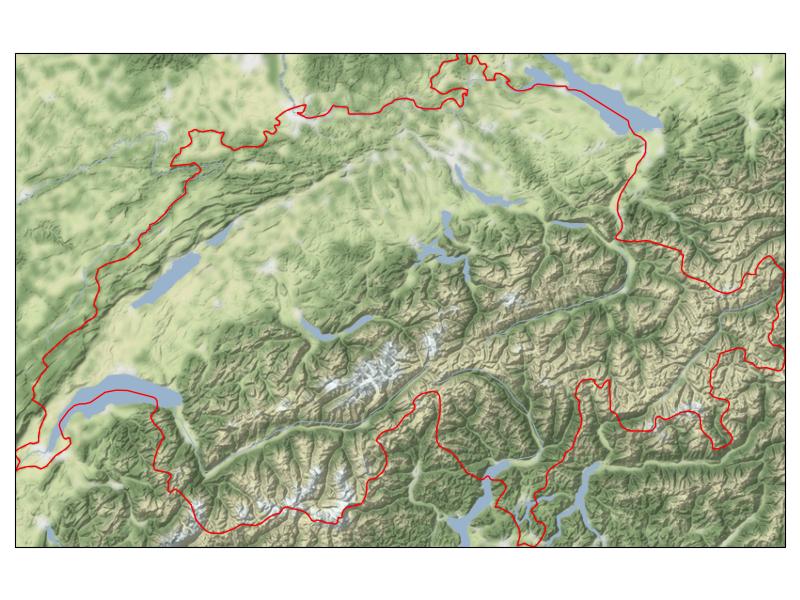
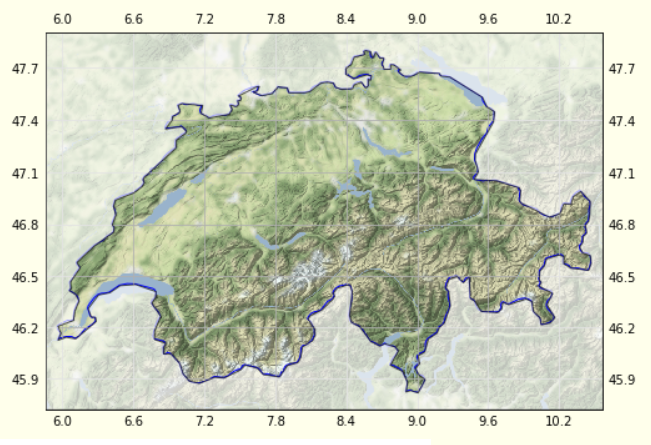
You need a mask to hide the un-wanted part of the image. Here is a runnable code that demonstrates all the steps to get the intended plot.
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
from cartopy.io import shapereader
import cartopy.io.img_tiles as cimgt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import geopandas
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def rect_from_bound(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax):
"""Returns list of (x,y)'s for a rectangle"""
xs = [xmax, xmin, xmin, xmax, xmax]
ys = [ymax, ymax, ymin, ymin, ymax]
return [(x, y) for x, y in zip(xs, ys)]
# request data for use by geopandas
resolution = '10m'
category = 'cultural'
name = 'admin_0_countries'
shpfilename = shapereader.natural_earth(resolution, category, name)
df = geopandas.read_file(shpfilename)
# get geometry of a country
poly = [df.loc[df['ADMIN'] == 'Switzerland']['geometry'].values[0]]
stamen_terrain = cimgt.Stamen('terrain-background')
# projections that involved
st_proj = stamen_terrain.crs #projection used by Stamen images
ll_proj = ccrs.PlateCarree() #CRS for raw long/lat
# create fig and axes using intended projection
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1, projection=st_proj)
ax.add_geometries(poly, crs=ll_proj, facecolor='none', edgecolor='black')
pad1 = .1 #padding, degrees unit
exts = [poly[0].bounds[0] - pad1, poly[0].bounds[2] + pad1, poly[0].bounds[1] - pad1, poly[0].bounds[3] + pad1];
ax.set_extent(exts, crs=ll_proj)
# make a mask polygon by polygon's difference operation
# base polygon is a rectangle, another polygon is simplified switzerland
msk = Polygon(rect_from_bound(*exts)).difference( poly[0].simplify(0.01) )
msk_stm = st_proj.project_geometry (msk, ll_proj) # project geometry to the projection used by stamen
# get and plot Stamen images
ax.add_image(stamen_terrain, 8) # this requests image, and plot
# plot the mask using semi-transparency (alpha=0.65) on the masked-out portion
ax.add_geometries( msk_stm, st_proj, zorder=12, facecolor='white', edgecolor='none', alpha=0.65)
ax.gridlines(draw_labels=True)
plt.show()
The resulting plot:
![enter image description here]()
and the mask:
![enter image description here]()
Edit1
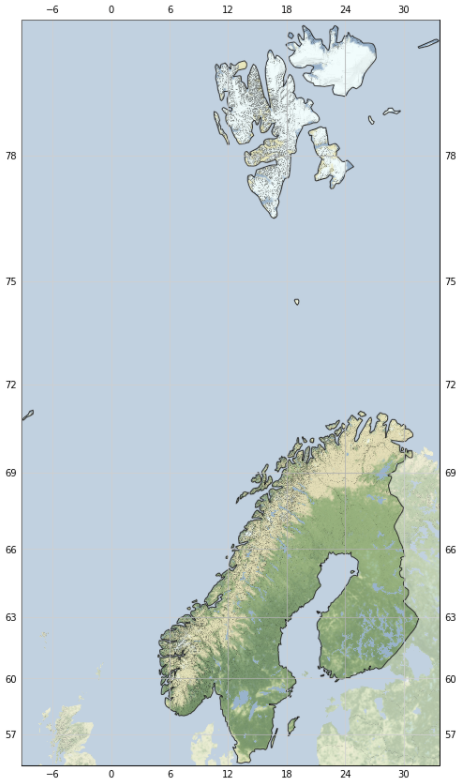
The code above is good for a single country. If multiple contiguous countries are our new target, we need to select all of them and dissolve into a single geometry. Only a few lines of code need to be modified.
Example: new target countries: ['Norway','Sweden', 'Finland']
The line of code to be replaced:
poly = [df.loc[df['ADMIN'] == 'Switzerland']['geometry'].values[0]]
New lines of code to replace:
scan3 = df[ df['ADMIN'].isin(['Norway','Sweden', 'Finland']) ]
scan3_dissolved = scan3.dissolve(by='LEVEL')
poly = [scan3_dissolved['geometry'].values[0]]
The sample output map:
![enter image description here]()