The ConcurrentDictionary<TKey,TValue> has no notion of order. When you enumerate it, you can't make any assumption regarding the order in which the keys will be emitted. You are not even allowed to assume that a single enumeration will yield unique keys. You could study the source code of the class and try to get a better understanding of how the keys are stored, but it will be a daunting task. Even worse, the value of this knowledge will evaporate as soon as the next version of the .NET runtime is released. Microsoft reserves the right to change the behavior of any API, as long as the affected behavior is not documented. And making the correctness of your program depend on implementation details of code that you don't control, is not something that most developers are comfortable with, and for good reasons.
Just for fun I wrote the demo below, that shows how the collection behaves for shuffled sequences that contains elements incremented by different steps:
for (int step = 1; step <= 10; step++)
{
Random random = new(0);
Console.WriteLine($"Step: {step}");
int[] source = Enumerable.Range(1, 15)
.OrderBy(_ => random.Next())
.Select(x => x * step)
.ToArray();
Console.WriteLine($"Source shuffled: [{String.Join(", ", source)}]");
Console.WriteLine($"Source ordered: [{String.Join(", ", source.Order())}]");
ConcurrentDictionary<int, string> dictionary = new();
foreach (int i in source) dictionary.TryAdd(i, null);
Console.WriteLine($"dictionary.Keys: [{String.Join(", ", dictionary.Keys)}]");
Console.WriteLine();
}
Output:
Step: 1
Source shuffled: [5, 10, 11, 8, 12, 14, 4, 6, 13, 1, 3, 2, 7, 9, 15]
Source ordered: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
dictionary.Keys: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
Step: 2
Source shuffled: [10, 20, 22, 16, 24, 28, 8, 12, 26, 2, 6, 4, 14, 18, 30]
Source ordered: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30]
dictionary.Keys: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30]
Step: 3
Source shuffled: [15, 30, 33, 24, 36, 42, 12, 18, 39, 3, 9, 6, 21, 27, 45]
Source ordered: [3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45]
dictionary.Keys: [33, 3, 36, 6, 39, 9, 42, 12, 45, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30]
Step: 4
Source shuffled: [20, 40, 44, 32, 48, 56, 16, 24, 52, 4, 12, 8, 28, 36, 60]
Source ordered: [4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60]
dictionary.Keys: [4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60]
Step: 5
Source shuffled: [25, 50, 55, 40, 60, 70, 20, 30, 65, 5, 15, 10, 35, 45, 75]
Source ordered: [5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, 65, 70, 75]
dictionary.Keys: [65, 35, 5, 70, 40, 10, 75, 45, 15, 50, 20, 55, 25, 60, 30]
Step: 6
Source shuffled: [30, 60, 66, 48, 72, 84, 24, 36, 78, 6, 18, 12, 42, 54, 90]
Source ordered: [6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60, 66, 72, 78, 84, 90]
dictionary.Keys: [66, 36, 6, 72, 42, 12, 78, 48, 18, 84, 54, 24, 90, 60, 30]
Step: 7
Source shuffled: [35, 70, 77, 56, 84, 98, 28, 42, 91, 7, 21, 14, 49, 63, 105]
Source ordered: [7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70, 77, 84, 91, 98, 105]
dictionary.Keys: [63, 35, 98, 7, 70, 42, 105, 14, 77, 49, 21, 84, 56, 28, 91]
Step: 8
Source shuffled: [40, 80, 88, 64, 96, 112, 32, 48, 104, 8, 24, 16, 56, 72, 120]
Source ordered: [8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 88, 96, 104, 112, 120]
dictionary.Keys: [32, 64, 96, 8, 40, 72, 104, 16, 48, 80, 112, 24, 56, 88, 120]
Step: 9
Source shuffled: [45, 90, 99, 72, 108, 126, 36, 54, 117, 9, 27, 18, 63, 81, 135]
Source ordered: [9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, 99, 108, 117, 126, 135]
dictionary.Keys: [63, 126, 36, 99, 9, 72, 135, 45, 108, 18, 81, 54, 117, 27, 90]
Step: 10
Source shuffled: [50, 100, 110, 80, 120, 140, 40, 60, 130, 10, 30, 20, 70, 90, 150]
Source ordered: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150]
dictionary.Keys: [130, 100, 70, 40, 10, 140, 110, 80, 50, 20, 150, 120, 90, 60, 30]
Online demo.
So apparently the ConcurrentDictionary<TKey,TValue> emits the keys in a sorted order when the step is 1, 2 or 4, otherwise there is no obvious order. Which is a useless knowledge, but there you have it!

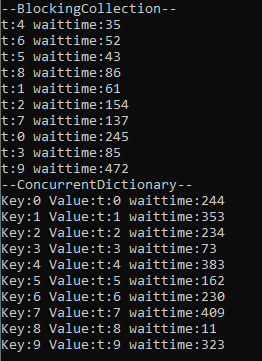
waittimeis a misnomer: it is a randomly generated value. What do you mean with "in thread order"? Items in dictionaries don't have an order, but it looks like thatConcurrentDictionaryiterates the keys in ascending order (that might be a coincedence). But iteration order usually has nothing to do with insertion order. – RarelyconcurrentDictionary.TryAdd(5, "five"); concurrentDictionary.TryAdd(1, "one");and then print it. Which order will the output be? (1, 5, …) – RarelyConcurrentDictionaryto give result likeBlockingCollection. @knittle I tried and it prints sorted. @Garrick and can we say thatConcurrentDictionaryalways sorts by key (regardless of insertion time)? – Philippeville