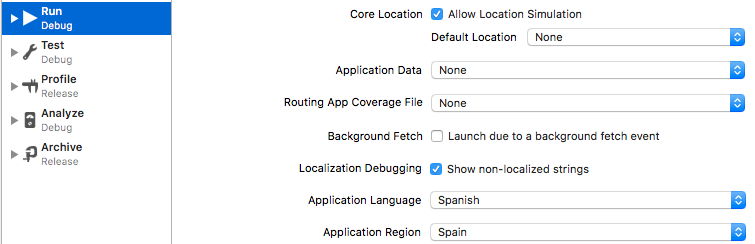
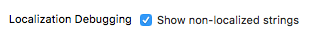
I'm not sure there is a straight answer to your question directly so I'm providing you with some additional ideas on how to solve your problem. I use the structures below to test all my string localisations but only that they resolve to a valid dictionary entry, not what that dictionary entry actually contains. However, I believe you could add the extra check without too much difficulty.
This applies to Swift only
I no longer use NSLocalizedString. Instead, I use a combination of a localised .plist ("Strings.plist" for want of a better name) file and an extension on String thus:
extension String {
var localized: String {
return EKTLocaliser.sharedInstance.localize(string: self)
}
}
The EKTLocaliser object referenced above looks like this:
final class EKTLocaliser: NSObject {
static let sharedInstance : EKTLocaliser = {
let instance = EKTLocaliser()
return instance
}()
private var localizableDictionary: NSDictionary
private override init() {
self.localizableDictionary = [:]
}
func setDictionary(lDict: NSDictionary) {
self.localizableDictionary = lDict
}
func localize(string: String) -> String {
guard let localizedString = ((localizableDictionary.value(forKey: string) as AnyObject).value(forKey: "value") as? String) else {
assert(true, "Missing translation for: \(string)")
return "--"
}
return localizedString
}
}
This localised class requires that each entry in the .plist file is a dictionary with a "value" key (there is also a "comment" key where you can put a note for the translator but the localiser object is not dependent on the comment)
Here is an example of one entry in the Base (.plist) dictionary:
![Base localisation example entry]()
In your application code you can use this construct (depends, see below):
myLabel.text = someTextString.localized
Now to your point regarding unit testing. In your unit test, you can instantiate an instance of the localizer, load a .plist dictionary into it and you have full access to all of your localised strings. The specific .plist that you load will depend on which localisation you are wanting to test. You can get a list of all localisations in your project from the main bundle thus:
self.availableLanguages = Bundle.main.localizations
Then, using that list, load each localisation dictionary (and test) in turn thus:
if let dict = loadDictionary(root: self.availableLanguages[i]) {
self.stringLocaliser?.setDictionary(lDict: dict)
}
else {
XCTFail("Cannot load Base localisation dictionary")
}
where loadDictionary is:
func loadDictionary(root: String) -> NSDictionary? {
if let path = Bundle.main.path(forResource: root + ".lproj/Strings", ofType: "plist") {
return NSDictionary(contentsOfFile: path)
}
else {
assertionFailure("Cannot instantiate path for Strings.plist")
}
return nil
}
Finally, I create enum constants for all keys into the localisation dictionary and iterate over the enum to test all strings. The only testing that I do is to verify that the localisation resolves to a valid dictionary entry but you could extend this to test that it resolves to what you expect (i.e., the correct translation):
enum Ls:String {
case kLearnShu = "shu"
case kLearnHa = "ha"
case kLearnRi = "ri"
case kLearnExercise1 = "ex1"
case kLearnExercise2 = "ex2"
case kLearnExercise3 = "ex3"
}
The unfortunate thing with this enum approach is that it is invasive in your code. Instead of writing
mLabel.text = kLearnExercise1.localized
you have to write:
myLabel.text = Ls.kLearnExercise1.rawValue.localized
which is an unfortunate pain. Maybe there is a better way out there...
Ah, final point... iterating over a Dictionary is a bit seat-of-the-pants but I use this code from other postings on SO. As it is only test code and never appears in your application itself, I'm OK using it.
func iterateEnum<T: Hashable>(_: T.Type) -> AnyIterator<T> {
var i = 0
return AnyIterator {
let next = withUnsafeBytes(of: &i) { $0.load(as: T.self) }
if next.hashValue != i { return nil }
i += 1
return next
}
}
Hope that gives you some ideas...
Acknowledgments and respect to all the SO postings from which I cobbled together this approach...