So first of all, what are streams?
Well, with streams we can process meaning read and write data piece by piece without completing the whole read or write operation. Therefore we don't have to keep all the data in memory to do these operations.
For example, when we read a file using streams, we read part of the data, do something with it, then free our memory, and repeat this until the entire file has been processed. Or think of YouTube or Netflix, which are both called streaming companies because they stream video using the same principle.
So instead of waiting until the entire video file loads, the processing is done piece by piece or in chunks so that you can start watching even before the entire file has been downloaded. So the principle here is not just about Node.JS. But universal to computer science in general.
So as you can see, this makes streams the perfect candidate for handing large volumes of data like for example, video or also data that we're receiving piece by piece from an external source. Also, streaming makes the data processing more efficient in terms of memory because there is no need to keep all the data in memory and also in terms of time because we can start processing the data as it arrives, rather than waiting until everything arrives.
How they are implemented in Node.JS:
So in Node, there are four fundamental types of streams:
readable streams, writable streams, duplex streams, and transform streams. But the readable and writeable ones are the most important ones, readable streams are the ones from which we can read and we can consume data. Streams are everywhere in the core Node modules, for example, the data that comes in when an http server gets a request is actually a readable stream. So all the data that is sent with the request comes in piece by piece and not in one large piece. Also, another example from the file system is that we can read a file piece by piece by using a read screen from the FS module, which can actually be quite useful for large text files.
Well, another important thing to note is that streams are actually instances of the EventEmitter class. Meaning that all streams can emit and listen to named events. In the case of readable streams, they can emit, and we can listen to many different events. But the most important two are the data and the end events. The data event is emitted when there is a new piece of data to consume, and the end event is emitted as soon as there is no more data to consume. And of course, we can then react to these events accordingly.
Finally, besides events, we also have important functions that we can use on streams. And in the case of readable streams, the most important ones are the pipe and the read functions. The super important pipe function, which basically allows us to plug streams together, passing data from one stream to another without having to worry much about events at all.
Next up, writeable streams are the ones to which we can write data. So basically, the opposite of readable streams. A great example is the http response that we can send back to the client and which is actually a writeable stream. So a stream that we can write data into. So when we want to send data, we have to write it somewhere, right? And that somewhere is a writeable stream, and that makes perfect sense, right?
For example, if we wanted to send a big video file to a client, we would just like Netflix or YouTube do. Now about events, the most important ones are the drain and the finish events. And the most important functions are the write and end functions.
About duplex streams. They're simply streams that are both readable and writeable at the same time. These are a bit less common. But anyway, a good example would be a web socket from the net module. And a web socket is basically just a communication channel between client and server that works in both directions and stays open once the connection has been established.
Finally, transform streams are duplex streams, so streams that are both readable and writeable, which at the same time can modify or transform the data as it is read or written. A good example of this one is the zlib core module to compress data which actually uses a transform stream.
![enter image description here]()
*** Node implemented these http requests and responses as streams, and we can then consume, we can use them using the events and functions that are available for each type of stream. We could of course also implement our own streams and then consume them using these same events and functions.
Now let's try some example:
const fs = require('fs');
const server = require('http').createServer();
server.on('request', (req, res) =>{
fs.readFile('./txt/long_file.txt', (err, data)=>{
if(err) console.log(err);
res.end(data);
});
});
server.listen('8000','127.0.01', ()=>{
console.log(this);
});
Suppose long_file.txt file contain 1000000K lines and each line contain more thean 100 words, so this is a hug file with a big chunk of data, now in the above example problem is by using readFile() function node will load entire file into memory, because only after loading the whole file into memory node can transfar the data as a responce object.
When the file is big, and also when there are a ton of request hitting your server, by means of time node process will very quickly run out of resources and your app will quit working, everything will crash.
Let's try to find a solution by using stream:
const fs = require('fs');
const server = require('http').createServer();
server.on('request', (req, res) =>{
const readable = fs.createReadStream('./txt/long_file.txt');
readable.on('data', chunk=>{
res.write(chunk);
});
readable.on('end',()=>{
res.end();
})
readable.on('error', err=>{
console.log('err');
res.statusCode=500;
res.end('File not found');
});
});
server.listen('8000','127.0.01', ()=>{
console.log(this);
});
Well in the above example with the stream, we are effectively streaming the file, we are reading one piece of the file, and as soon as that's available, we send it right to the client, using the write method of the respond stream. Then when the next pice is available then that piece will be sent, and all the way until the entire file is read and streamed to the client.
So the stream is basically finished reading the data from the file, the end event will be emitted to signals that no more data will be written to this writable stream.
With the above practice, we solved previous problem, but still, there is a huge problem remain with the above example which is called backpressure.
The problem is that our readable stream, the one that we are using to read files from the disk, is much much faster than actually sending the result with the response writable stream over the network. And this will overwhelm the response stream, which cannot handle all this incoming data so fast and this problem is called backpressure.
The solution is using the pipe operator, it will handle the speed of data coming in and speed of data going out.
const fs = require('fs');
const server = require('http').createServer();
server.on('request', (req, res) =>{
const readable = fs.createReadStream('./txt/long_file.txt');
readable.pipe(res);
});
server.listen('8000','127.0.01', ()=>{
console.log(this);
});

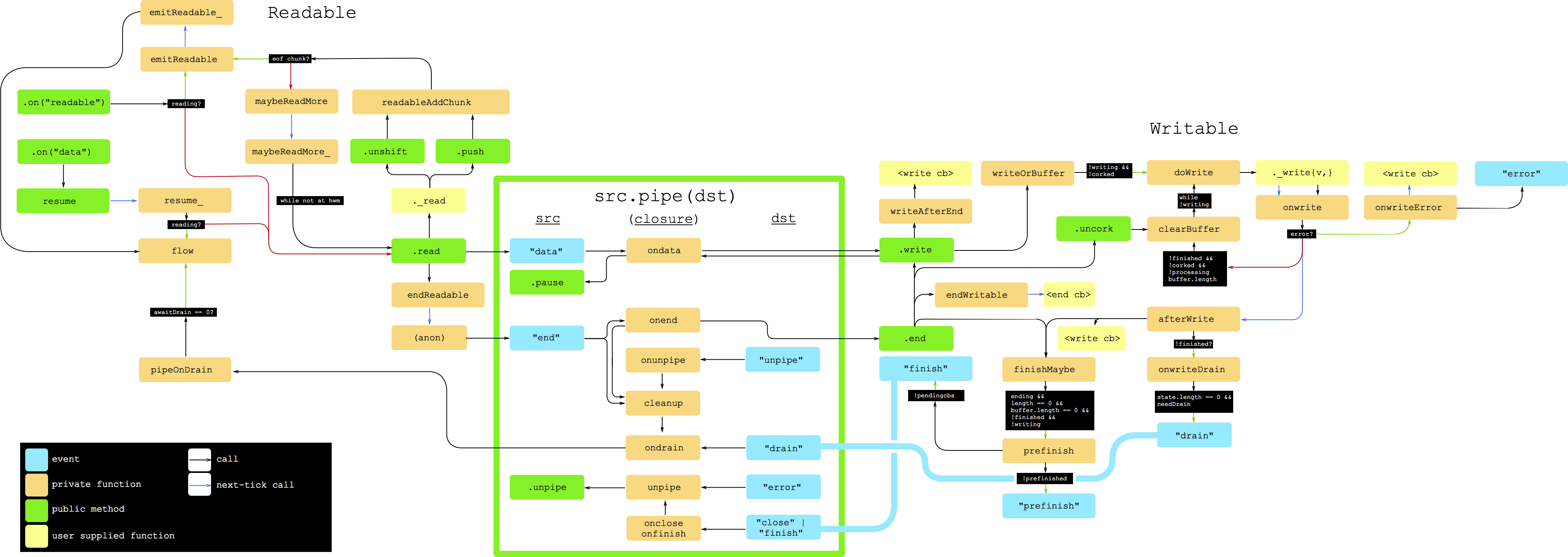

node. I am doing node for a while now and only seemed to have understood it this year. This also makes maintenance really hard, since only a few people understand the core part of it. I think they are mostly represented in the streams working group. Embracing the interface really changes the way you program and you'll utilize most of nodes power. I posted a diagram, which is really hard to google below. – Inhalant