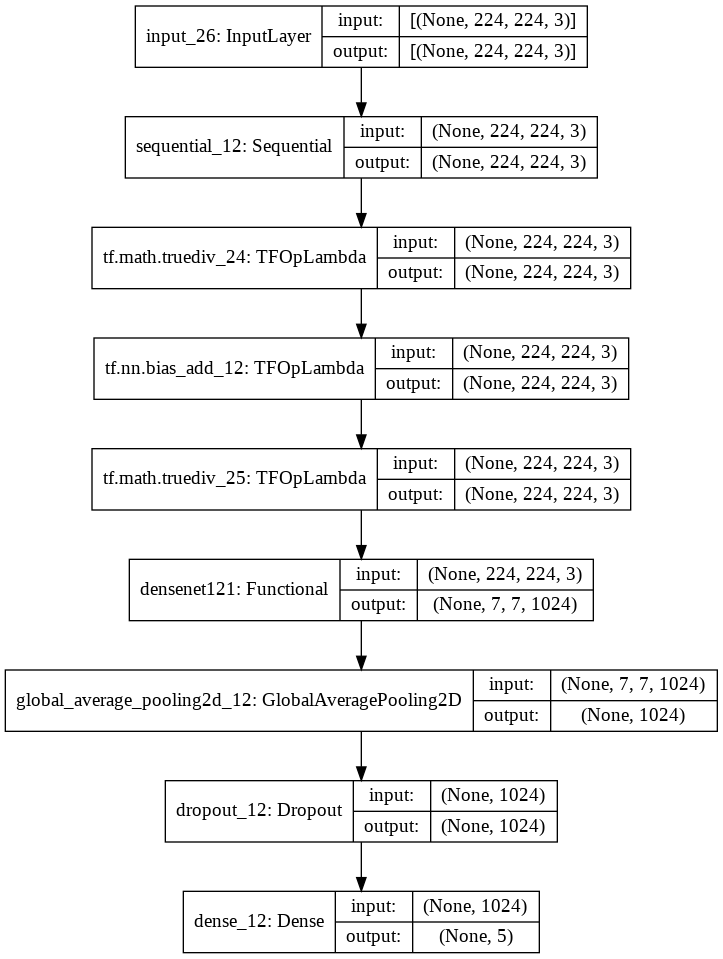
I get an error using gradient visualization with transfer learning in TF 2.0. The gradient visualization works on a model that does not use transfer learning.
When I run my code I get the error:
assert str(id(x)) in tensor_dict, 'Could not compute output ' + str(x)
AssertionError: Could not compute output Tensor("block5_conv3/Identity:0", shape=(None, 14, 14, 512), dtype=float32)
When I run the code below it errors. I think there's an issue with the naming conventions or connecting inputs and outputs from the base model, vgg16, to the layers I'm adding. Really appreciate your help!
"""
Broken example when grad_model is created.
"""
!pip uninstall tensorflow
!pip install tensorflow==2.0.0
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
IMAGE_PATH = '/content/cat.3.jpg'
LAYER_NAME = 'block5_conv3'
model_layer = 'vgg16'
CAT_CLASS_INDEX = 281
imsize = (224,224,3)
img = tf.keras.preprocessing.image.load_img(IMAGE_PATH, target_size=(224, 224))
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img)
img = tf.io.read_file(IMAGE_PATH)
img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img)
img = tf.cast(img, dtype=tf.float32)
# img = tf.keras.preprocessing.image.img_to_array(img)
img = tf.image.resize(img, (224,224))
img = tf.reshape(img, (1, 224,224,3))
input = layers.Input(shape=(imsize[0], imsize[1], imsize[2]))
base_model = tf.keras.applications.VGG16(include_top=False, weights='imagenet',
input_shape=(imsize[0], imsize[1], imsize[2]))
# base_model.trainable = False
flat = layers.Flatten()
dropped = layers.Dropout(0.5)
global_average_layer = tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()
fc1 = layers.Dense(16, activation='relu', name='dense_1')
fc2 = layers.Dense(16, activation='relu', name='dense_2')
fc3 = layers.Dense(128, activation='relu', name='dense_3')
prediction = layers.Dense(2, activation='softmax', name='output')
for layr in base_model.layers:
if ('block5' in layr.name):
layr.trainable = True
else:
layr.trainable = False
x = base_model(input)
x = global_average_layer(x)
x = fc1(x)
x = fc2(x)
x = prediction(x)
model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs = input, outputs = x)
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-4),
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
This portion of the code is where the error lies. I'm not sure what is the correct way to label inputs and outputs.
# Create a graph that outputs target convolution and output
grad_model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs = [model.input, model.get_layer(model_layer).input],
outputs=[model.get_layer(model_layer).get_layer(LAYER_NAME).output,
model.output])
print(model.get_layer(model_layer).get_layer(LAYER_NAME).output)
# Get the score for target class
# Get the score for target class
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
conv_outputs, predictions = grad_model(img)
loss = predictions[:, 1]
The section below is for plotting a heatmap of gradcam.
print('Prediction shape:', predictions.get_shape())
# Extract filters and gradients
output = conv_outputs[0]
grads = tape.gradient(loss, conv_outputs)[0]
# Apply guided backpropagation
gate_f = tf.cast(output > 0, 'float32')
gate_r = tf.cast(grads > 0, 'float32')
guided_grads = gate_f * gate_r * grads
# Average gradients spatially
weights = tf.reduce_mean(guided_grads, axis=(0, 1))
# Build a ponderated map of filters according to gradients importance
cam = np.ones(output.shape[0:2], dtype=np.float32)
for index, w in enumerate(weights):
cam += w * output[:, :, index]
# Heatmap visualization
cam = cv2.resize(cam.numpy(), (224, 224))
cam = np.maximum(cam, 0)
heatmap = (cam - cam.min()) / (cam.max() - cam.min())
cam = cv2.applyColorMap(np.uint8(255 * heatmap), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
output_image = cv2.addWeighted(cv2.cvtColor(img.astype('uint8'), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR), 0.5, cam, 1, 0)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(output_image)
plt.show()
I also asked this to the tensorflow team on github at https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/37680.