Here's the definition of CFG from Wikipedia, I know you already know this but for the sake of completeness I'm putting it here
A control flow graph (CFG) in computer science is a representation,
using graph notation, of all paths that might be traversed through a
program during its execution.
Ref: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Control_flow_graph
Following is the definition of a Path
Path: a sequence of node on the CFG (static), including an entry node
and an exit node; path segment: a subsequence of nodes along the path
Ref: http://web.cs.iastate.edu/~weile/cs513x/4.ControlFlowAnalysis.pdf
So the reason for drawing one would be to determine all possible paths taken by the program, which may help us determine things like test coverage without actually running the program (static analysis).
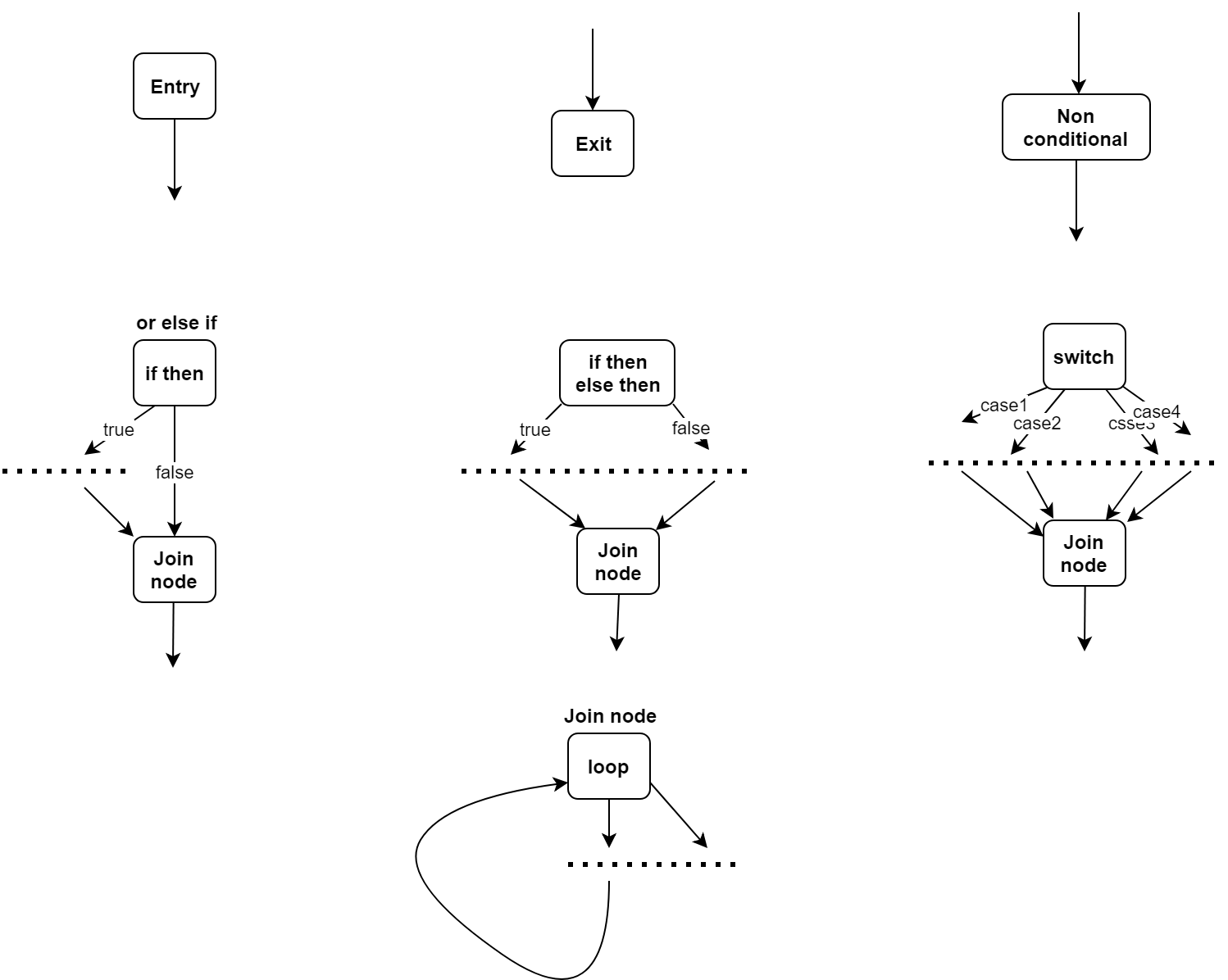
Following are the simple rules that we can follow to draw a CFG
- Any statement will be a node in graph
- All nodes have a directed edge either coming to them or going out of them or both. Entry node (first statement) has only outgoing edges and Exit node has only incoming edges.
- only conditional statements like
if/else if, switch, loops would have more than one outgoing edges.
- All paths coming out of a node will converge at some point, in worst case they converge on Exit.
Here's a cheat sheet which explains it better
![CFG cheat sheet]()
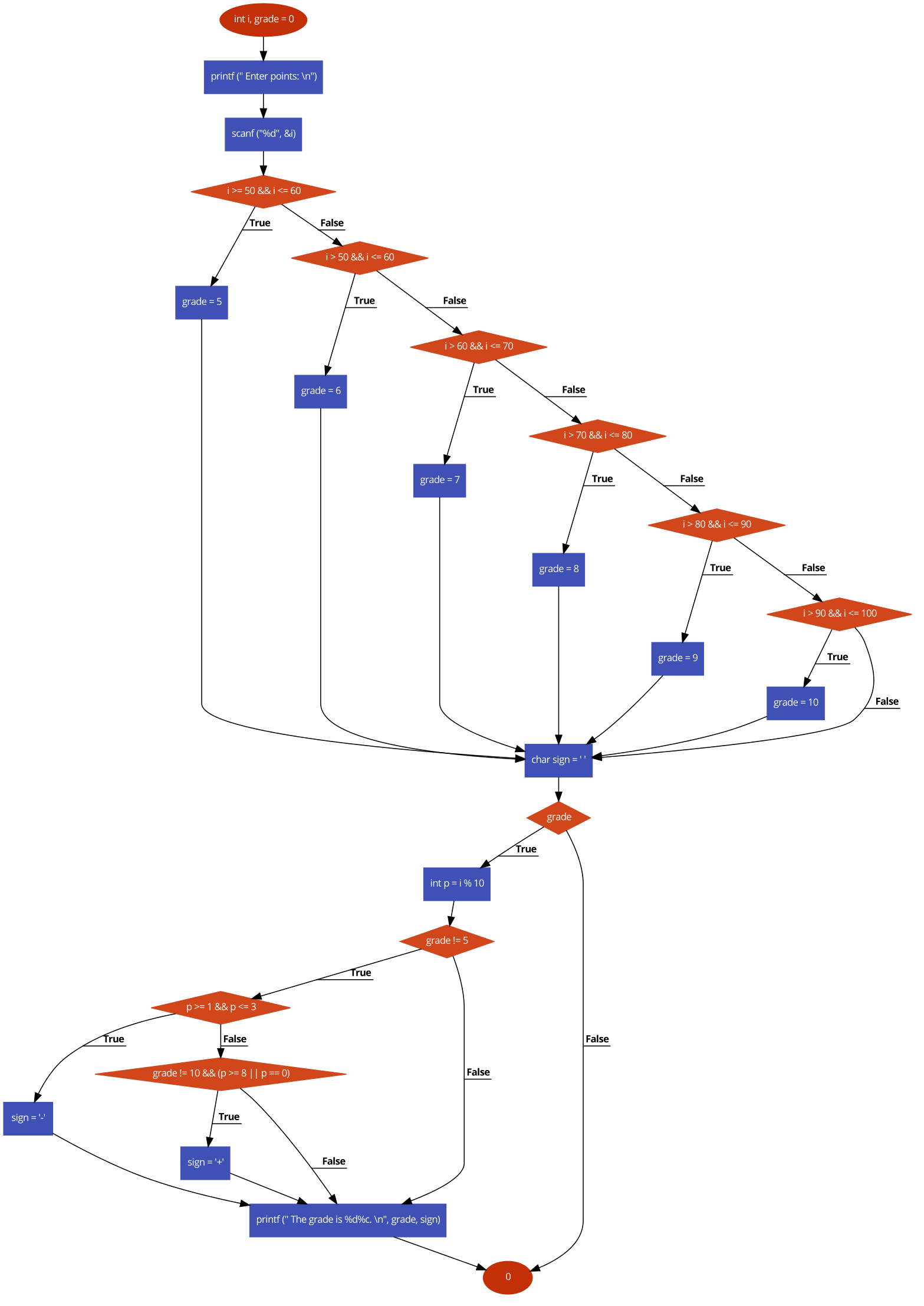
Now lets map every statement in your program to an number that we'll use to denote CFG nodes
int main() {
1. int i, grade = 0;
2. printf (" Enter points: \n");
3. scanf ("%d", &i);
4. if (i >= 50 && i <= 60)
5. grade = 5;
6. else if (i > 50 && i <= 60)
7. grade = 6;
8. else if (i > 60 && i <= 70)
9. grade = 7;
10. else if (i > 70 && i <= 80)
11. grade = 8;
12. else if (i > 80 && i <= 90)
13. grade = 9;
14. else if (i > 90 && i <= 100)
15. grade = 10;
16. char sign = ' ';
17. if (grade) {
18. int p = i % 10;
19. if (grade != 5) {
20. if (p >= 1 && p <= 3)
21. sign = '-';
22. else if (grade != 10 && (p >= 8 || p == 0))
23. sign = '+';
}
24. printf (" The grade is %d%c. \n", grade, sign);
}
25. return 0;
}
Here's the output created by following the directions from cheat sheet diagram above. Notice that node 16 and 24 are acting as join node for many conditional nodes before.
![enter image description here]()
Credit: I have used draw.io to create images posted above.
Note: Secret to drawing a CFG is to treat every statement independent to the program, draw it and then link it's entry and exit to the rest of the graph.
Following are a few initial steps that I followed
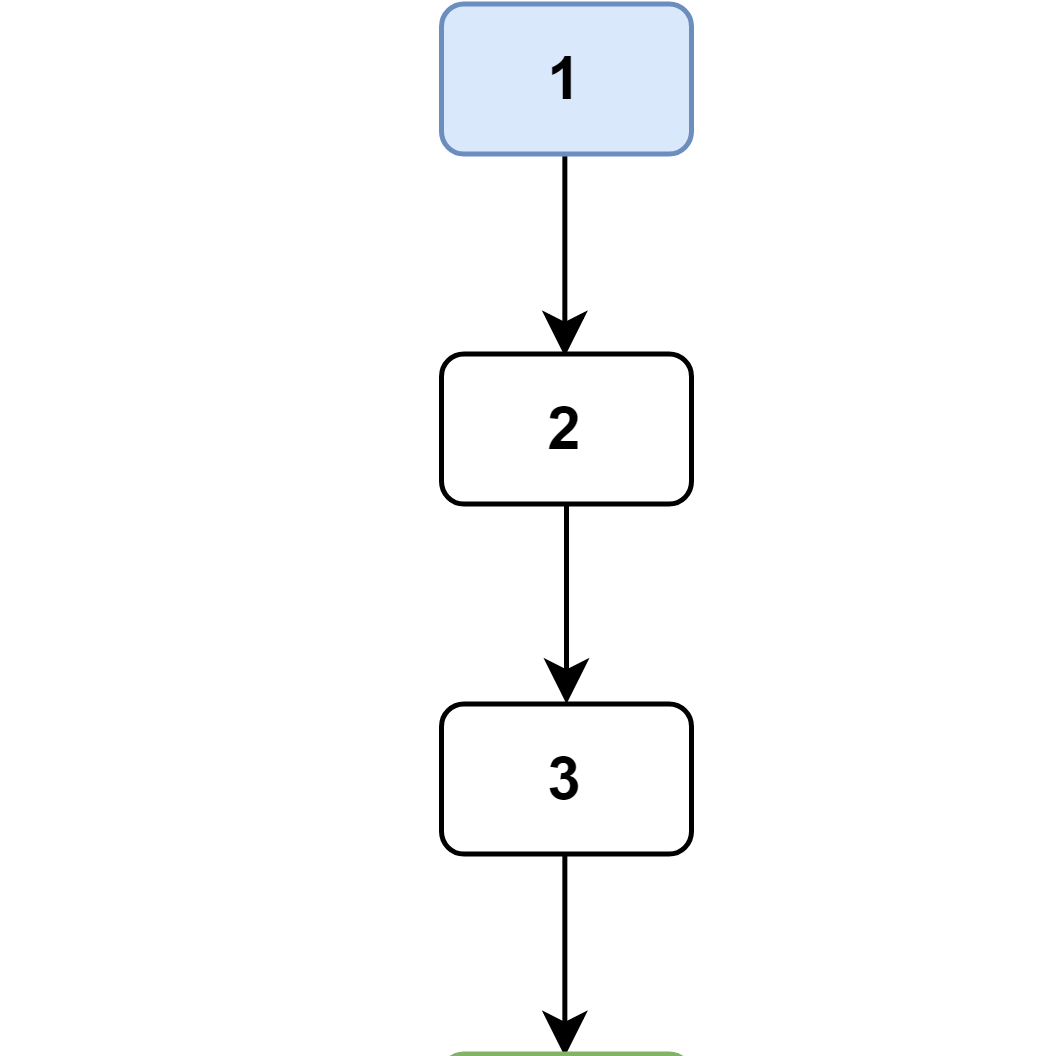
- Statement 1, 2, and 3 are non conditional so I created three blocks linking them together.
![step1]()
- Statement 4 is a conditional statement. So I have to create 4 blocks for it. First for for statement 4, second and third for TRUE, FALSE edges, and lastly one for JOIN node. If true then statement 5 is run if not then we go to statement 6. From statement 5 we directly go to statement 16, which is our join node. Finally we link block 4 to bock 3's out going edge.
![enter image description here]()
- Now statement 6 itself is a conditional statement so we again need 4 blocks for it. We already have one for itself block 6. Join node for it will be statement 16 as if it's condition is true then statement 7 is run and it directly goes to 16. Now we already have block 6 and 16 so we just need blocks for TRUE, FALSE branches which are statement 7 and 8.
![step3]()
And so on, we keep checking the cheat sheet for the applicable nodes and create them in isolation then link then with previous nodes.