I am using Ubuntu on WSL2 (not on Docker Desktop).
According to How to fix docker ‘Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?’ on Ubuntu, I can automatically start the docker daemon at boot using
sudo systemctl enable docker
instead of just starting it again at every boot with
sudo systemctl start docker
with both commands avoiding "Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?".
When using any of the two, I get
Synchronizing state of docker.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable docker
and a test run shows, that docker is not yet running:
docker run hello-worlddocker: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?. See 'docker run --help'.
Some steps before, I also got a different message at this point:
System has not been booted with systemd as init system (PID 1). Can't operate.Failed to connect to bus: Host is down"
which brought me to Fixing "System has not been booted with systemd as init system" Error:
Reason: Your Linux system is not using systemd How to know which init system you are using? You may use this command to know the process name associated with PID 1 (the first process that runs on your system):
ps -p 1 -o comm=It should show systemd or sysv (or something like that) in the output.
ps -p 1 -o comm= gave me init.
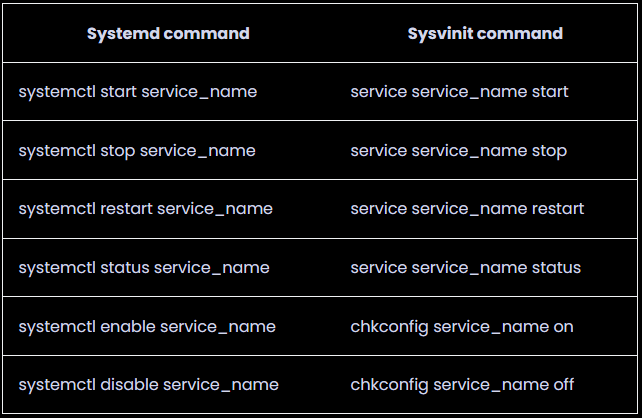
According to this and this table
Systemd command
Sysvinit command
systemctl start service_name
service service_name start
systemctl stop service_name
service service_name stop
systemctl restart service_name
service service_name restart
systemctl status service_name
service service_name status
systemctl enable service_name
chkconfig service_name on
systemctl disable service_name
chkconfig service_name off
I can choose service docker start to run docker, which works. But I cannot find something like "systemd"'s sudo systemctl enable docker for "sysvinit". I would expect it to be like:
sudo service docker enable
But that "enable" is not available for "sysvinit" / "init".
While sudo service docker start works like sudo systemctl start docker, there is no such command that uses "enable". At the moment, I need to run sudo service docker start whenever I start WSL2.
The question:
What is the command that reaches sudo systemctl enable docker using sudo service docker ..., or if that does not exist, what is a workaround here to automatically start docker when opening Ubuntu on WSL2?